It is no secret that everyone loves a good story. And when that story is played out onscreen, it can captivate and enchant us even more so.
But whether you are just watching a film on your couch, dabbling in the world of movie production, or simply want to know more about the process and terminology that brings stories to life on the screen, there is always something to learn about film!
And because the film industry is so wide ranging and varied, there is a vast amount of terminology that goes into the making, enjoying, and critiquing of films.
This is your ultimate glossary of all the terms that are behind the production of your favorite films, so sit back, grab your popcorn, and read on to learn more.

Abby Singer (shot)
This is a nickname for the second-to-last shot of the day during the shooting of a film. The name was attributed to famed American production manager and assistant film director Abby Singer between the 1950s-1980s. The very last shot of the day is known as the martini shot.
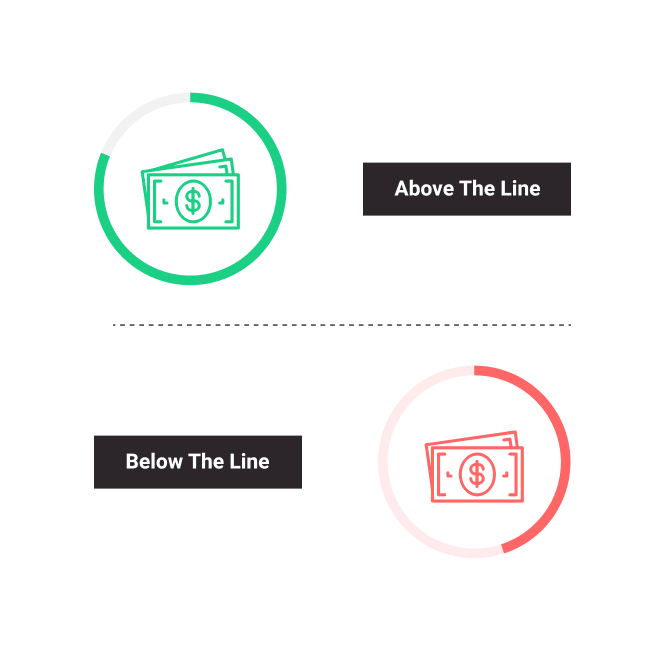
Above the Line
The term refers to the film’s budget that covers the costs associated with major creative talents involved in the production—including the actors, director, producer(s), and writer(s). Films that have heavy reliance on special effects and computer graphics usually have more above the line budget costs because of the technical aspects and their requirements. The opposite of this term is below the line.

Abstract (form)
This is a type of film that rejects traditional narrative in favor of using poetic form to convey its meaning or feeling, often through the use of color, motion, sound, irrational images, or unconventional visuals. These films can also be known as non-linear, or avant-garde.
Act
Divisions within the plot of a film are called acts. A film is often divided by ‘plot points’ during moments of dramatic change. Long films are divided mid-way with an intermission.

Action
This term has a three-fold meaning:
1. Referring to any rehearsed movement or series of events that take place before the camera and propel the story forward toward its conclusion.
2. The word called out (via a megaphone) by the director at the start of the current take during filming to alert actors to begin performing.
3. Referring to the main component of action films, that often contain significant amounts of action, adventure, and violence.

Actor
Referring to any male or female who plays a character role in a film. Some alternate gender-neutral terms include player, artist, or performer.
Adaptation
This term describes the presentation of one art form through another medium. Film adaptations are derived from an original source such as a stage play, short story, book, article, history, novel, video game, comic strip/book, etc. A close adaptation tries to preserve the setting, dialogue, and overall feel of the original source.

Aerial Shot
These shots are filmed from far overhead as from a helicopter, blimp, balloon, plane, drone, kite, or other aerial device. Alternately, some aerial shots use miniatures or are created with CGI. Aerial shots are a variation on the crane shot. If the aerial shot is at the opening of a film, it is referred to as an establishing shot.

A-List or A-Level
Referring to top-tier actors/actresses who are paid upwards of $20 million per feature film. This can also refer to top producers, directors and writers who can be guaranteed make and release a film.

Alan Smithee Film
When directors want to disassociate themselves with a film, they will use the pseudonym Alan Smithee, alternatively Alan Smithee Jr., Allan Smithee, or Allen Smithee.

Allegory
An allegory is basically an extended metaphor. This is when a film draws specific attention to and suggests a relationship between a visible part of the film, such as a character, setting, or event, and an abstract meaning outside of the film itself.
(Jordan Peele’s Us Is a Bone-Chilling Allegory for Generation X)

Alternate Ending
This refers to shooting or re-shooting a film’s ending for its theatrical release, for any number of reasons, be it test audience preview results, controversial or unpopular subject matter, or to provide a ‘happy’ ending. Also known as a director’s cut.
Ambience
The emotional current of a particular scene or setting, and the feeling or mood it evokes.
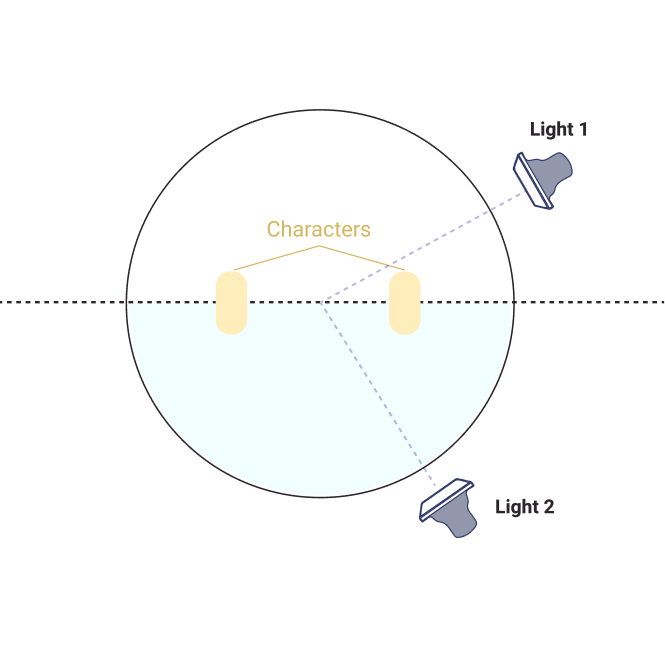
Ambient Lighting
Natural light or surrounding light around the scene’s subject, giving it a usually soft background lighting.

Anachronism
An object, artifact, or element in a film that is out of its historic or natural time or place.

Ancillary Rights
This is the agreement that dictates what percentage of the merchandising profits is allocated to individuals involved in production. Merchandising products include books, action figures, posters, collectables, décor, etc.
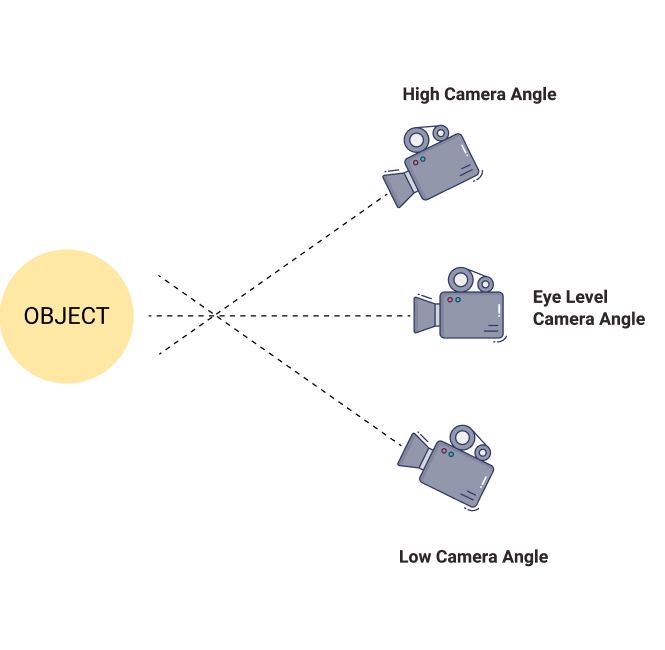
Angle
The perspective a camera uses to capture its subject. The camera angle can be used with other specific shots, such as high, low, oblique, etc.
Angle On
This refers to directing the camera to move along with and focus onto a certain subject.

Animation
The type and process of filmmaking where inanimate objects or individual drawings (either by hand or CGI) are shot frame by frame to create the appearance of a sequence of motion. Animation types include Claymation, computer animation, and stop-motion.

Anime
A style of Japanese film and television animation that has its roots in Japanese comic books known as manga. It typically involves colorful graphics, vibrant characters, action-orientated plots, and often a fantastic or futuristic theme and setting. Anime also covers a wide array of genres. Hayao Miyazaki is one of the more prominent and famous directors of anime films for adult audiences.

Antagonist
The main character in a film that is in adversarial conflict with the film’s hero or main protagonist, this ‘bad guy’ helps provide the conflict that pushes the narrative forward to its conclusion. The antagonist role can also be a group, society, nature, force, or spirit.

Anti-Hero
This type of protagonist lacks the typical attributes of a traditional hero archetype, such as character defects, confusion, eccentricities, or ambiguous morals. These characters can be sympathetic, existing outside the mainstream and often challenging it.

Aperture
The measurement of the opening in a camera lens, regulating the amount of light that can pass through the lens and make contact with the film inside. Aperture is a part of the exposure triad along with shutter speed and ISO.
Arc Shot
This refers to filming the subject through a moving, encircling camera.

Art Director
The individual in the art department in charge of a film set’s feel, look, construction, and design. This includes being responsible for the number and types of props and their placement on the set.

Art-House Films
These are films that are not mainstream, but are thought to hold artistic value, often low-budget, independent, or foreign. They can be found playing in niche art-house theaters.
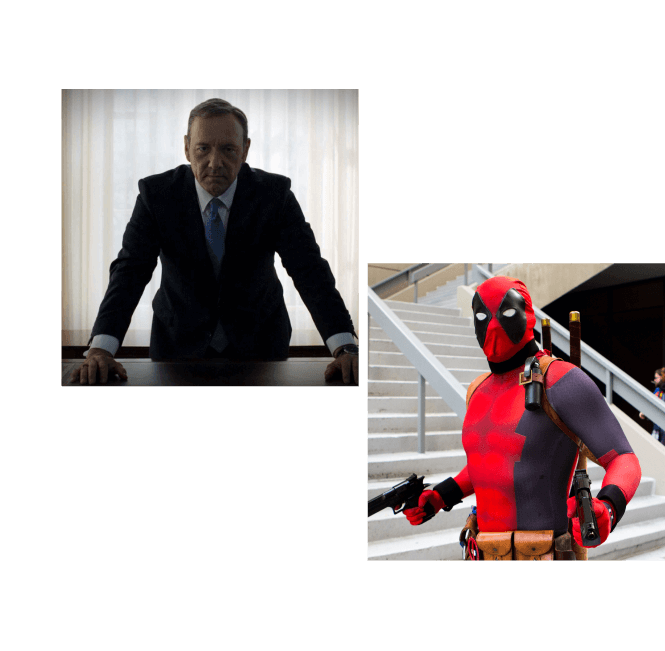

Aside
This refers to a character breaking the fourth wall in a film, when they address the audience beyond the screen directly and momentarily break the illusion of filmic isolation. Characters like Deadpool and Frank Underwood commonly use this.

Aspect Ratio
The ratio of a film describes the measurement of the projected image’s width to its height. The standard for Hollywood theatrical releases is 1.65:1. Shapes may vary, from the television standard, a nearly square ratio of 1.33:1 to a very long rectangle. In European cinema, the typical aspect ratio is 1.66:1. Historically, in the 1950s, Hollywood tried to draw in new audiences by developing different kinds of widescreen systems like Cinerama and CinemaScope, both of which average 2.35:1.
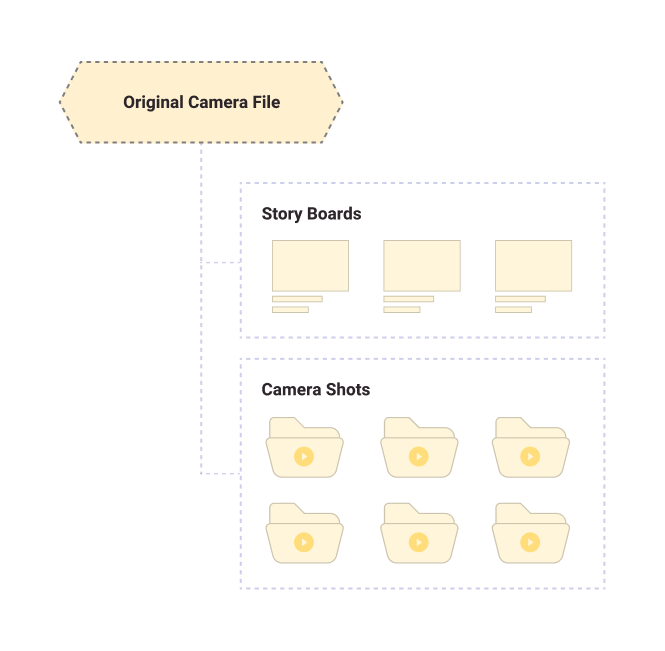
Assembly
Arranging camera shots in accordance with the order of the script and sequence of the story boards in the first step of editing.

Asynchronism
Refers to the disparity between what is seen and what is heard on screen. At its most dramatic, asynchronous sound is contrapuntal and contrasts with the image. For example, asynchronous sound would be seeing a door slamming on screen while you hear a dog bark as the sound effect. Sergei Eisenstein supported contrapuntal or asynchronous sound as a part of his larger theory of dialectical montage.
Available Light
This is the naturally available light at an off-set location. Shots tend to look more realistic when natural light is used over artificial light.

Audition
The process that actors go through to land a role. They present a prepared reading or a cold read to a director or casting agent, in order to showcase their talents and their fit for the character and the film. After the initial audition, the actor might be called back for additional readings or run-throughs before knowing if they have gotten the part.
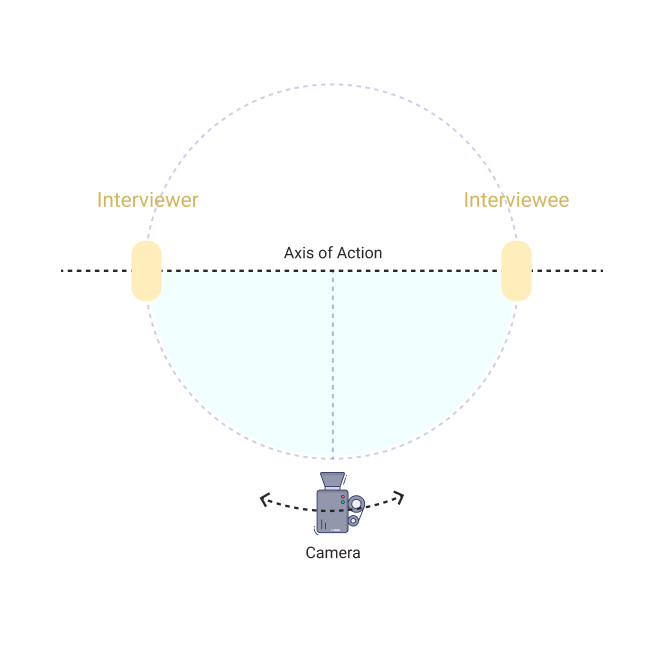
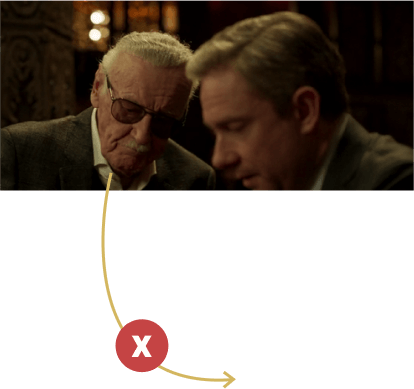
Axis of Action
This term refers to the imaginary line that passes between the primary actors in a scene. This line determines the spatial relationships between all the elements in the scene as being either left or right to the actors and helps to maintain order in the scene geography. Also known as the 180-degree line

B-Movie
Term for a low-budget, offbeat, or generally bad film, usually from independent producers. B-Movies have become infamous for their campy content, low-grade special effects, catchy titles, and bad acting.

Background Artist
This person can also be known as a matte artist, and is responsible for designing a visual backdrop to fill in the background of a scene. While these backgrounds were historically created using paint, backdrops today are mainly created digitally.

Back Lot
The land on a film studio’s property where filmmakers can shoot outdoor scenes for less cost than travelling to on-location sites. You can also tour the backlots at major studios in Los Angeles.

Back Story
The events directly preceding the beginning of the film’s narrative or storyline. This gives information that helps fill out characters, events, settings, and motivations.
Balance
This is an overarching term that includes how the light, sound, and movement all work together in a scene. It also refers to the composition, aesthetic quality, and how well the elements all work together in a film.
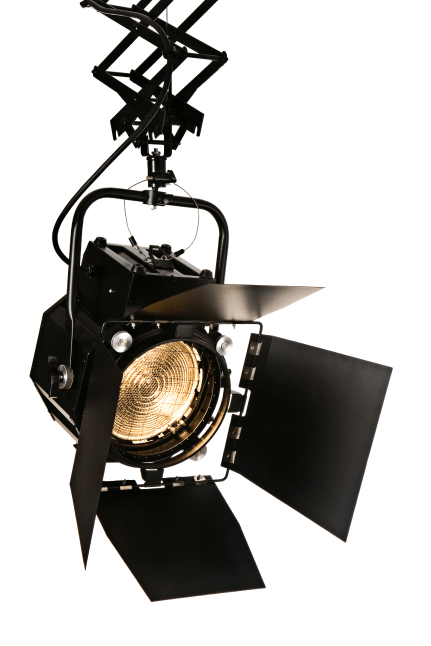

Barn Doors
These are metal folding doors on all sides of a lighting fixture, able to be moved on their hinges in order to direct lighting for a particular shot.
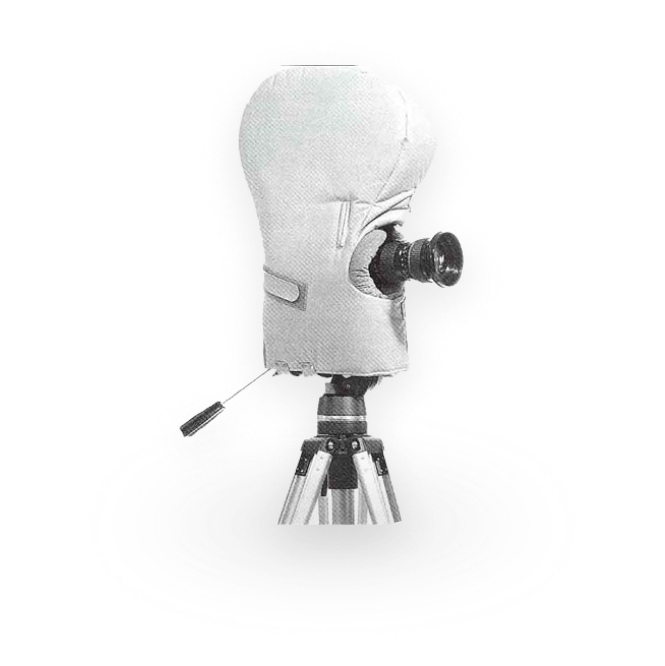
Barney
Referring to a sound-minimizing blanket to be placed over the camera to reduce the noise emitted from its moving parts.

Based on a True Story
This refers to a film that contains elements of historical or real-life basis. It may only contain a few factual elements. These films can be based on biographies, historic events or timelines, and more, with situations or characters altered for greater dramatic effect onscreen.

Behind the Scenes
The events or circumstances off-camera and during filmmaking. Often, these outtakes can be found as bonus watchable content when the DVD or digital download of the film is purchased.
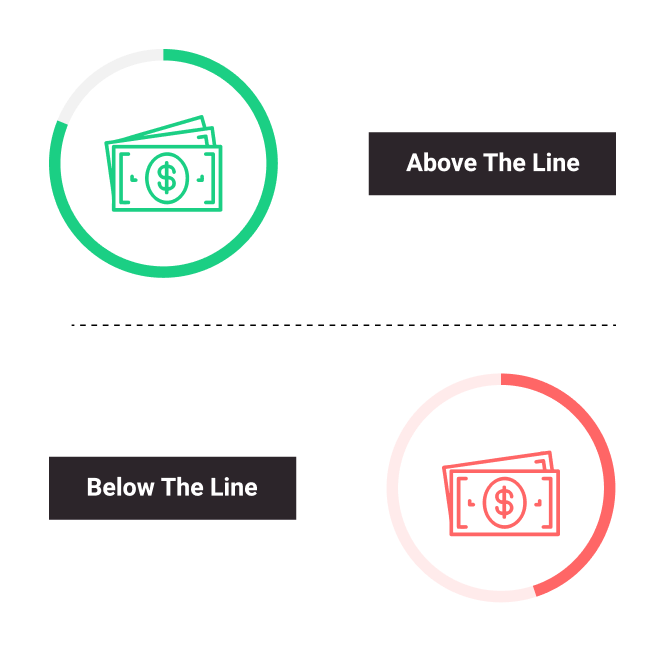
Below the Line
All production costs not included in above the line expenses, such as music rights, material costs, publicity, trailer, marketing, etc.

Best Boy
This role is the aide, assistant, or technical assistant for the key grip or gaffer, responsible for coiling and routing all power cords needed to run lights and lighting, and may also schedule what persons and equipment are needed on any given shoot date.

Billing
Referring to the placement of names of actors, directors, and producers on movie posters, marquees, and other publicity materials. Generally, the most prominent actor will have the top billing position with larger lettering, followed by the second most prominent. Filmmakers and studios rely on these materials as box-office draws, letting the actors’ names bring in the audiences.

Blimp
The housing for a camera intended to prevent the sound recording equipment from picking up any extra sounds that emit from the camera and could ruin the sound take.

Blockbuster
This refers to a standout film that is considered a major box office success. The new benchmark for a blockbuster film in the early 2000s was raised to more than $200 million in North America. Blockbuster films make the studio much more capital than was put into the making of it, not only being critically and publicly acclaimed but also bringing in a profit.
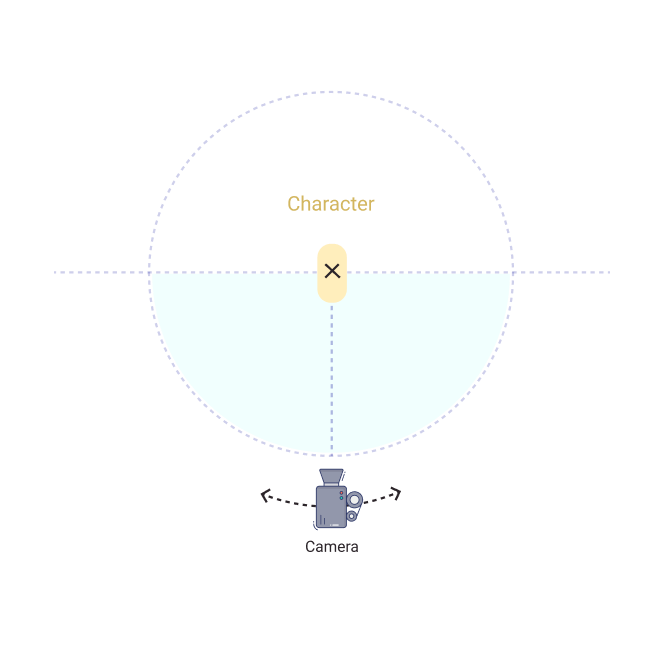
Blocking
Referring to where the actors will move and stand on set so that the lighting cues and camera placement can be decided and rehearsed.

Blue Screen (or Green Screen)
Blue or green screens are evenly-lit and monochromatic backdrops that actors can perform in front of. The screen is later replaced with the final background via chroma-keying and computer graphics. Films made today generally use blue or green screens to create the intricate or fantastical backgrounds the plot necessitates.

Body Double
An actor who takes the place of another actor in certain scenes and shots. As opposed to a stunt double, a body double is brought in for nude scenes when a big-name actor does not want to appear in the scene themselves and expose themselves.

Boom
This equipment is a travelling or moveable pole, arm, or telescopic extension device that can hold a microphone, light or camera. This boom is then suspended overhead above the scene and outside the frame when filming.

Boom Microphone
The person in charge of controlling the boom microphone.

Boom Operator
A long pole with a microphone attached to the end.
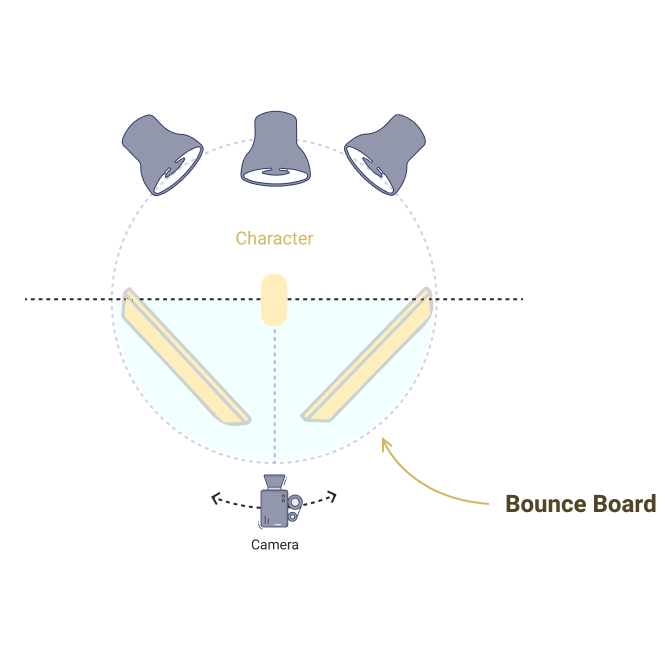
Bounce Board
Used to reflect soft light, this is a large white card made of foam or poster board.

Bracketing
This term refers to shooting the same scene with several different F-stops.

Call Sheet
The schedule for crew members over the course of production. This informs each department and their members when to arrive on set, and other crucial information. It also provides lists of what actors are appearing in which scenes.

Cameo
A brief appearance in a film by a famous actor, director or celebrity, who is not already cast in it. For example, Stan Lee was a frequent cameo in his Marvel films.
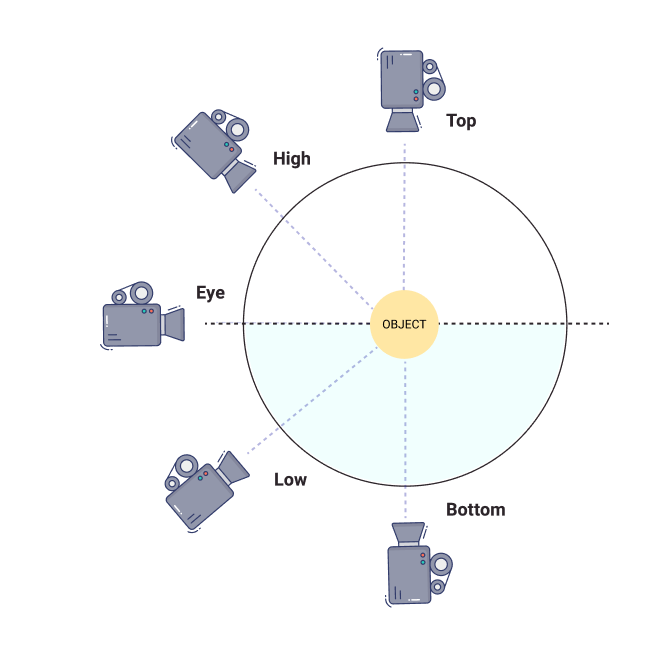
Camera Angle
The point of view for the shot that the camera operator chooses to photograph or film. Some basic angles include high, low, dutch, and eye-level.

Captions (or Subtitles)
The line of printed text that describes or translates the action or dialogue onscreen. Usually found at the bottom of the screen, captions are common in foreign language films shown in North America, and as an option in online streaming services for movies and TV shows. These are great resources for anyone deaf, hard-of-hearing, or simply wanting a descriptive experience of the media
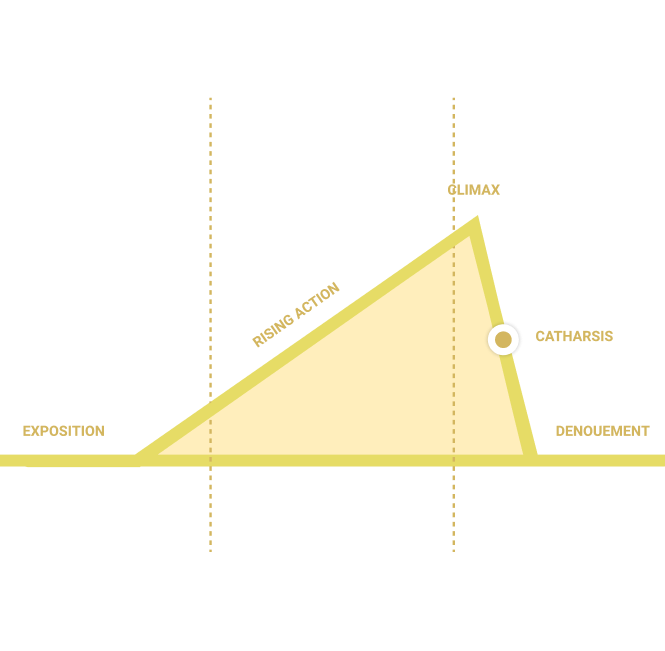
Catharsis
The point in a film’s climax where the audience collectively experiences a release of emotional tension that has been building throughout the plot, giving relief and restoration. A moment of catharsis can be when the hero becomes triumphant over the villain and the danger has been subdued.
Cel
This is a hand drawn sheet that represents a single frame of animation, and usually is made of a clear material such as cellulose.
Image Src: https://gifer.com/en/WgBA
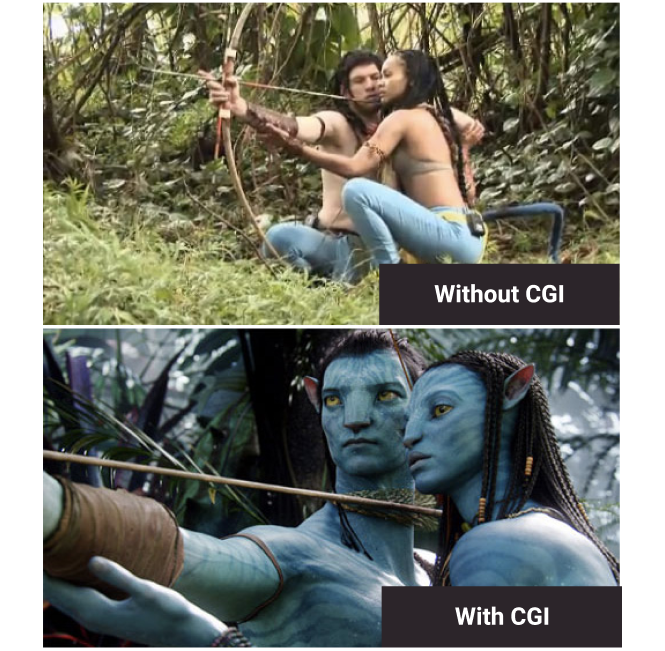

CGI (or Computer Generated Imagery)
Computer-generated content that can be special effects, entire characters, settings, creatures, and much more. With the rise in computer technology, CGI has become both more affordable and more realistic, leading film producers to lean more heavily on it for their productions.

Cheater Cut
This term refers to the introductory footage at the beginning of a TV series episode to overview what took place in the previous episode.

Cinematographer
The person with expertise in the art of capturing images on film stock or electronically, through the application of visual recording devices and the selection and arrangement of lighting systems. The chief cinematographer for a film is called the director of photography.

Cinema Verite
This is an approach to documentary film production which originated in France. It was made possible by the development of lighter-weight cameras and portable recording equipment that allow for smaller and portable crews. Instead of the director imposing their own views on the documentary production, the subject is allowed to speak and control the flow of narrative. This is a highly reflexive and self-conscious manner of documentary filmmaking which can acknowledge the presence of the director in the film as well as the subjects.

Clapperboard (or Clapboard)
Most commonly envisioned as the classic black-and-white board with a moveable arm at the top, this board is used to show information about the shot being filmed. Typically, the clapperboard contains the director’s name, title of the film, and the take being shot. Even though the traditional clapperboards can still be utilized, electronic ones have become more in style. These are also called slates or sticks.

Classical Editing
This type of editing is popular in Hollywood filmmaking, where the cuts and transitions are not invisible to the viewer, but are designed to be unobtrusive so that the audience does not necessarily notice them. Editing in this manner preserves a sense of narrative continuity but also allows for using cuts for emotional and dramatic purposes which do not necessarily advance the action.

Claymation
A method of filming figurines and models created out of clay or other moldable material, often through the use of stop-motion.
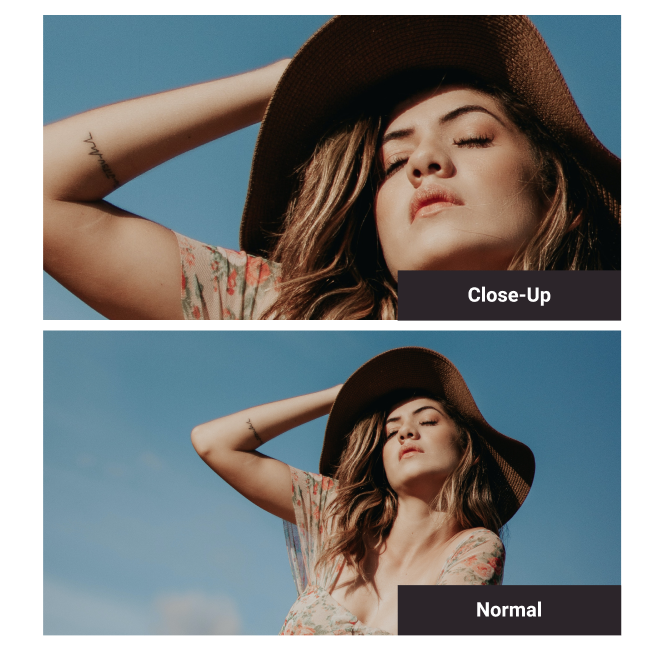
Close-Up
A detailed shot where the subject is larger than the frame, zooming in.
Colorization
The act of digitally altering a black and white film to a color film.

Coming-of Age Film
This is a term for a film that shows the journey of young people as they traverse into adulthood, through rites of passage that the audience can relate to. Typical hallmarks of these films include the loss of innocence, defining sexual identities, childhood dreams, and the determination of personal identity as the characters move from being children to adults.

Composition
This refers to the arrangement of all the elements of a shot in relation to the frame and the framing of the set.

Continuous
Referring to action moving through various locations without interruptions.

Continuity
A type of editing to ensure the story and action flows as seamlessly as possible, uninterrupted.
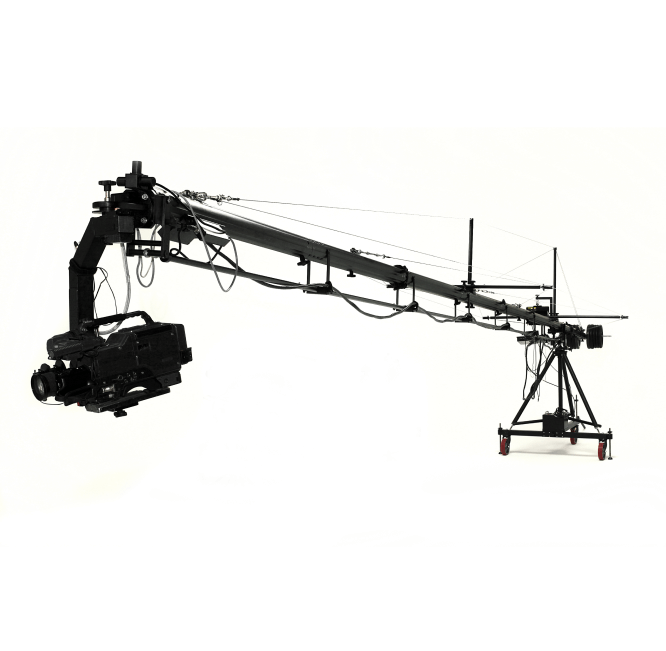
Crane Shot
A shot taken from a crane, a device resembling a large mechanical arm. This crane carries the camera and cameraman and is incredibly mobile, able to move in just about any direction.
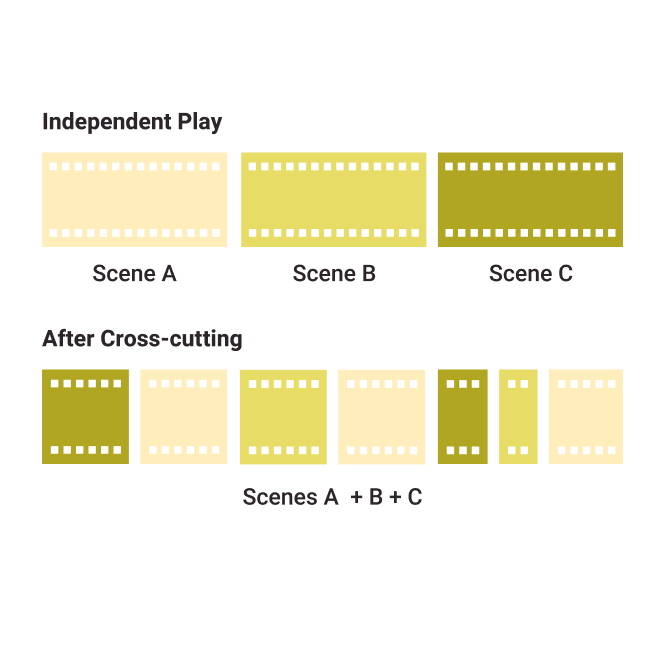
Cross-Cutting
This is the process of alternating two different scenes, typically in different locations, to suggest the idea of parallel action. Also called inter-cutting or parallel editing.
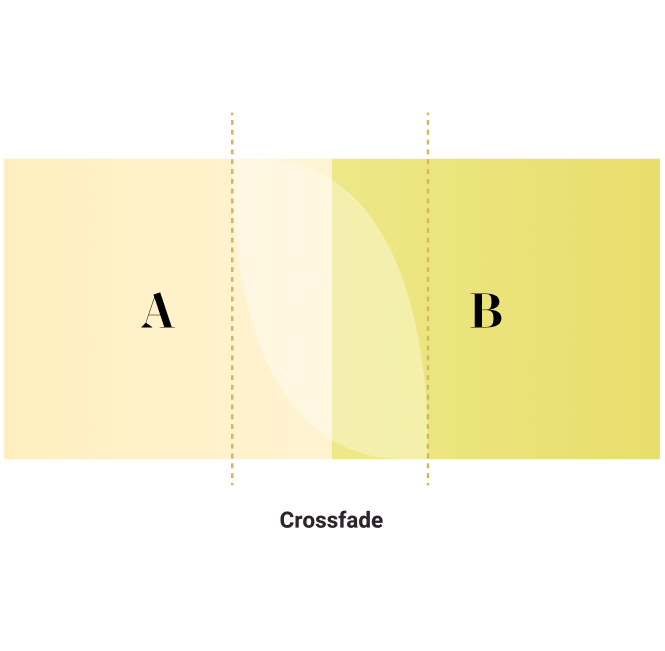
Crossfade
The process of one scene fading out and the fade into the next scene, with a moment of interruption between the scenes.

Cut
This term refers to a change in camera angle or placement, location, or time. “Cut” is also called by the director during the act of filming to indicate the current take is complete.
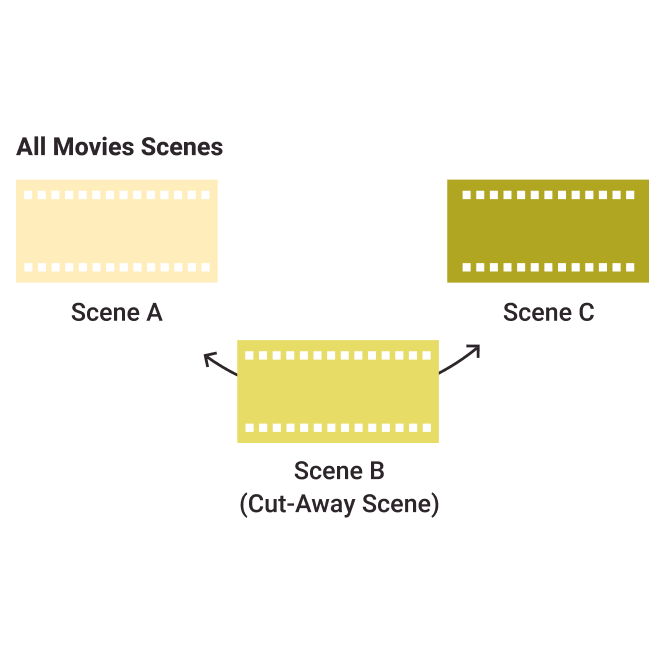
Cut-Away
A short duration shot that is supposed to take place at the same time as the main action but is not directly involved in the main action of the film.
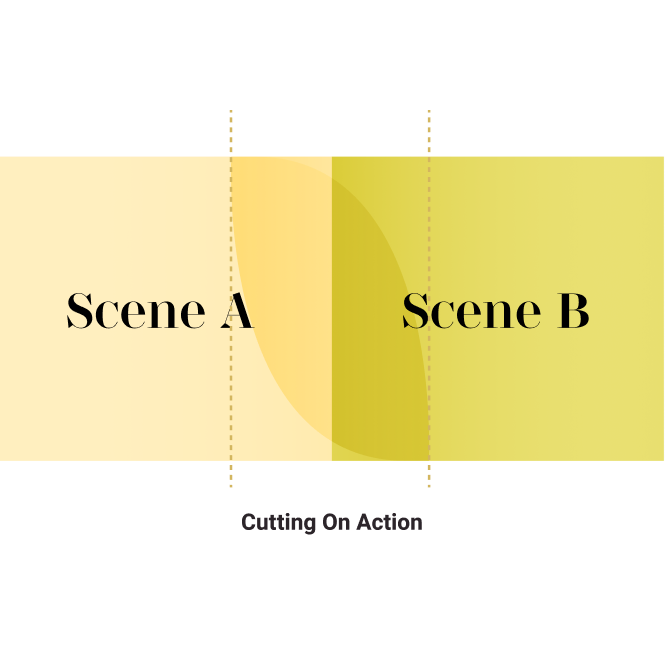
Cutting On Action
This refers to cutting from one shot to another view that either carries or matches a movement and gives the impression of a continuous time span. Because the action begins in one shot and is carried over to the next shot, a visual bridge is created that distracts viewers from noticing the cut in action.
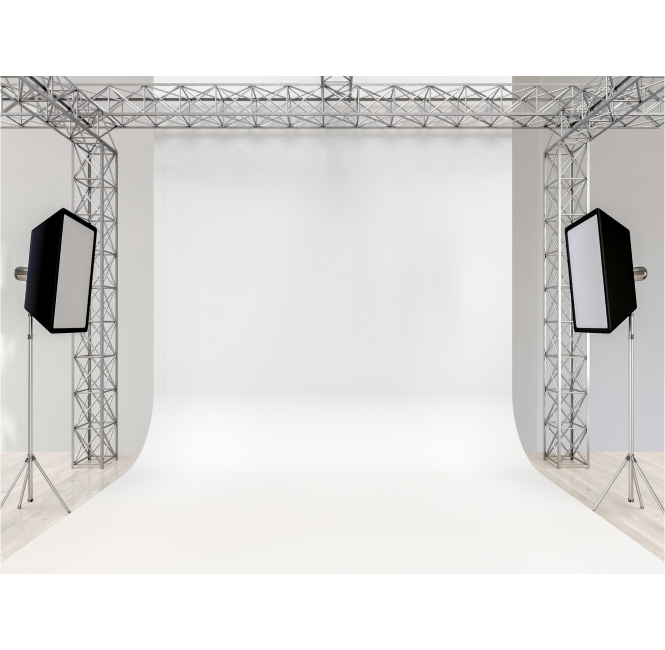

Cyclorama
A floor-to-ceiling, curved backdrop used on set to create a background for the scene, typically used to represent the sky on studio sets.
Dailies
This term refers to the rough, unedited cuts of the day (or from the previous day), where the director reviews them and decides if he wants to schedule a re-shoot or not.
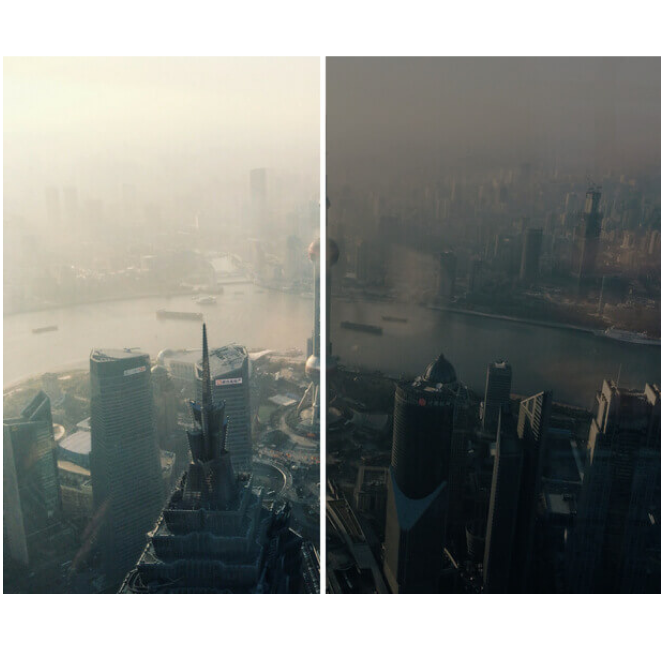

Day-For-Night
A type of lighting where the scene is shot in the daytime with daylight, and then through the use of filters the scene is darkened to look like night.
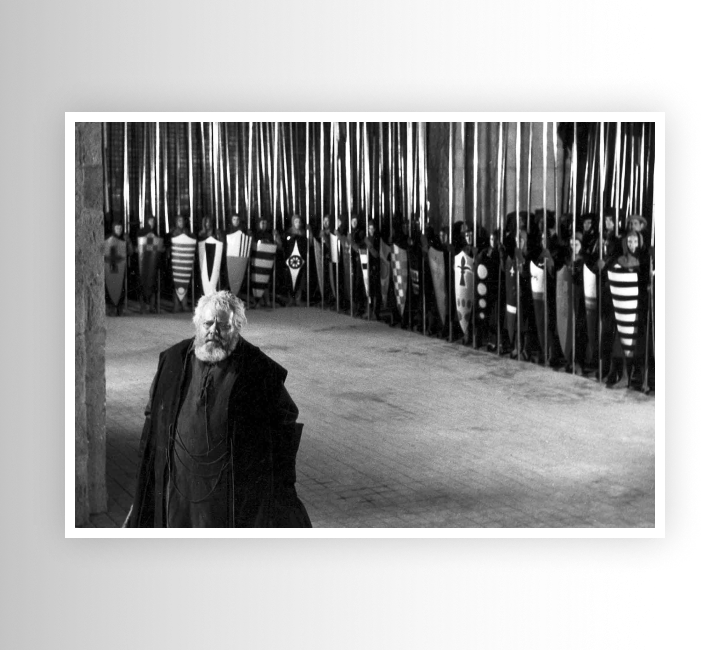

Deep Focus
When objects in the immediate foreground, the midground, and far distance or background, all appear in equally sharp focus at the same time.
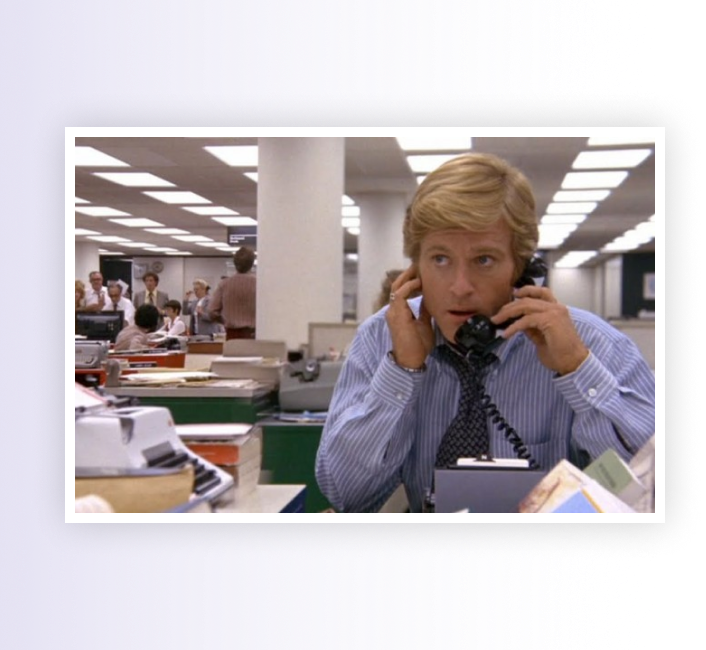

Deep Focus Shot
An exceptionally deep field for a particular shot.

Diegesis
In the world of the film’s story and narrative, this term refers to all events that characters are aware of or that have taken place in the history of the story, including spaces that are not shown on screen.
Diegetic Sound
Any speech, sound effects, or music that originates from a source within the world of the film’s story and narrative.

Diffusion
The process of putting materials in front of the light source to reduce its harshness, such as filters, glass, mesh, etc.

Directing the Eye
Emphasis on what is important in the shot by the use of lighting.

Direct Cinema
This is an approach to documentary filmmaking popularized by American filmmakers in the early 1960s. In this type of film production, the filmmaker simply observes and records the subjects and action and allows the meaning to evolve out of the footage. It is also characterized by use of natural lighting, a shoulder-mounted camera, and direct sound. One example of this is Frederick Wiseman’s “High School”.

Direct Sound
The sound that is captured and recorded during the filming. If used to refer to a style, these films do not add components like sound effects or dialogue on the postproduction stage.

Director
The principal creative artist on the film set, typically the driving artistic force behind the film process, and is responsible for communicating to the actors how the particular scene should be played.

Director’s Cut
This is the first fully-edited version of a film, before any outside parties like film studios have intervention.

Dissolve
This refers to the slow fade-out of one shot and the gradual fade-in of the next shot. The two images typically merge as a superimposition of images at the midpoint.

Documentary
This is a style of nonfiction film that explores, documents, and records the real world and utilizes actual events and real people as its raw footage.

Dunning
This is the shot taken from a moving vehicle, or from a hand-held travelling machine, giving a smooth and fluid movement shot.

Dutch Tilt (or Dutch Angle)
This refers to a camera shot that is composed by having the horizon not being parallel to the bottom of the frame.

DVD
This stands for a digital versatile disc or digital video disc. A DVD is an optical disc that functions as data storage for a film.
Dynamic Frame
The method of narrowing and widening of the frame to fit into a specific ratio for the scene being filmed.

Ellipsis
Referring to any periods of time left out of the film’s onscreen narrative. Special editing transitions indicate the passage of time for this eliding, often using a fade or dissolve transition.

Establishing Shot
A long shot that introduces the spatial relations among important characters, objects, and settings in an entire film or in a scene. Often an aerial shot that orients the audience for the next scene.
Image Src: https://www.nfi.edu/establishing-shot/

Executive Producer
This is the person in charge of production and oversees all of it, though not involved in technical aspects. They are usually involved in the business and finance realm of filmmaking.

Exposure
This term refers to the technical process of subjecting photographic film stock to light intensity for a given time, resulting in an image once the film stock has been processed.

Extreme Close-Up
A shot that is incredibly close-up and pictures a portion of the subject. Often used to showcase actors’ eyes, mouth, or other part of them.

Extremely Long Shot
A shot where the camera is placed at an extreme distance from the subject or object.

Eye-Level Shot
This is a shot taken at the subject’s or the director’s eye level, normally between 5 and 6 feet, but will change according to the director’s discretion and cultural or narrative contex.

Eyeline Match
This filming method creates the illusion of a character looking at an object or subject by cutting between two shots.
Fade-In
This filming method creates the illusion of a character looking at an object or subject by cutting between two shots.
Image Src: https://blog.hubspot.com/website/css-fade-in

Fast Motion
Any action that appears faster on screen than it could occur in real life. This is a special effect shot that is achieved by undercranking, or at less than 24 frames per second in sound, or 16-2 frames per second in silent film.

Favor On
Focusing or highlighting a specific action, object, or subject in a shot.

Film Gauge
This refers to the width of a piece of film stock and is measured in millimeters. Typical film gauges are as follows: home movies tend to be 8mm or super-6mm, low-budget films are usually shot in 16mm, feature films are usually shot in 35nmt, and some big-budget films are released in 70mm.
Film Stock
The medium in a camera where photographic images are recorded.
Image Src: https://gifer.com/en/A62i

Fisheye Lens
This is an extreme wide-angle lens that distorts the edges of an image, causing them to seem warped into a sphere.

Flashback
The technique in storytelling that allows a character to recall events previous to that moment in the film.
Flash Cut
Referring to a very swift shot that has a nearly subliminal effect, these shots can be as short as one frame.
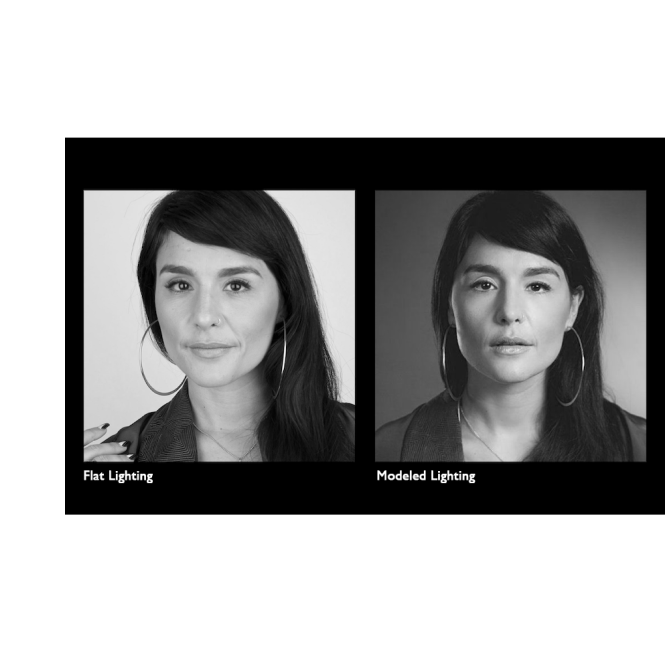

Flat Lighting
This type of lighting does not have contrasts in brights and darks.
Focus
This term refers to the degree of sharpness of an image, as well as the adjustment of the lens to create a sharper image. Further focus techniques are classed as deep focus, shallow focus, soft focus, follow focus, and rack focus, and all refer to different types of focusing.

Foley
The method of recreating incidental sound effects like footsteps or door closing in sync with the visual components of the film.

Follow Focus
The camera might have to be refocused during a shot if the camera or subject moves, in order to keep the subject in focus. When done smoothly, the moving subject will always stay in focus, and a zoom lens is often used to make this happen.

Fourth Wall
An imaginary plane that separates characters and action of the film from the audience. When the character ignores this boundary, it is known as breaking the fourth wall.
Image Src: https://www.primogif.com/p/m0zPewPq5MJNu
Framing
This refers to the manner in which the shot is composed, and how the subjects and objects on set are framed by the film image itself. The camera works to adjust to the character’s movements and keep them onscreen, centered, and in the frame.
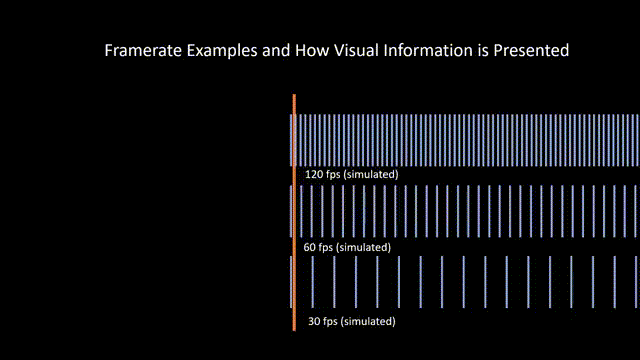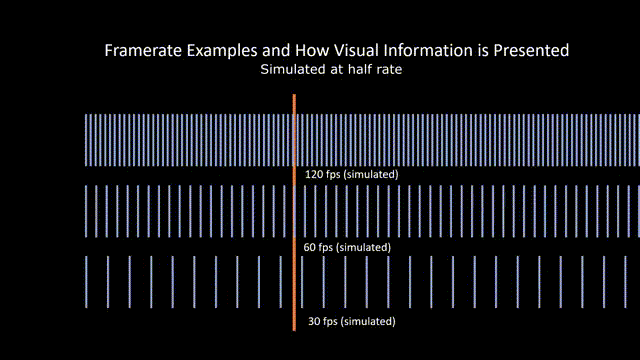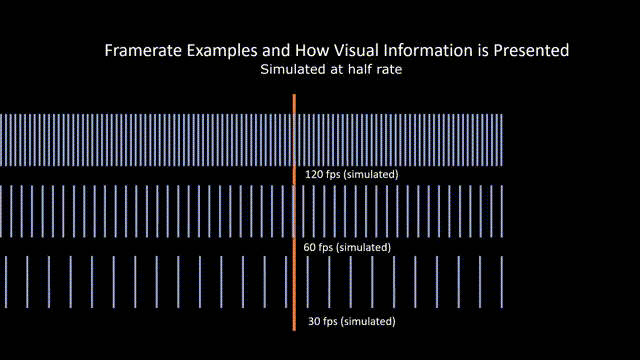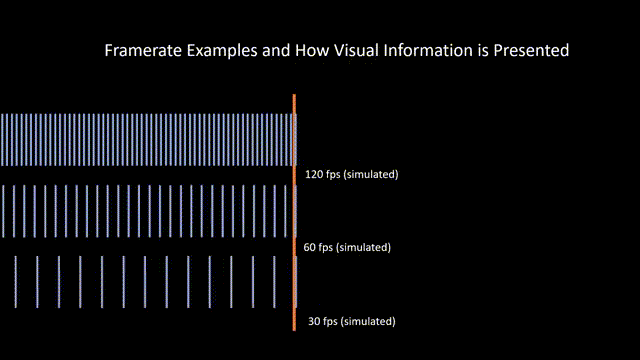
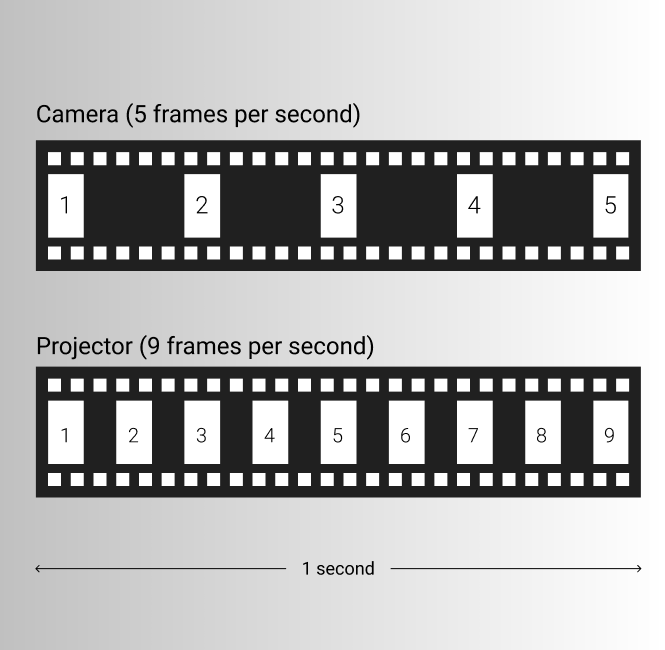
Frame Rate
Referring to the rate at which film stock passes in front of the camera aperture during filming. Higher frame rate shots appear slowed down during projection, and lower frame rate shots appear unnaturally fast during projection. This is also known as frames per second (FPS).
Image Src: https://gfycat.com/granularrealisticbobwhite

Freeze Frame
This is a special effect shot that gives the effect of a halt in action or still photo, accomplished by printing one frame multiple times with an optical printer.
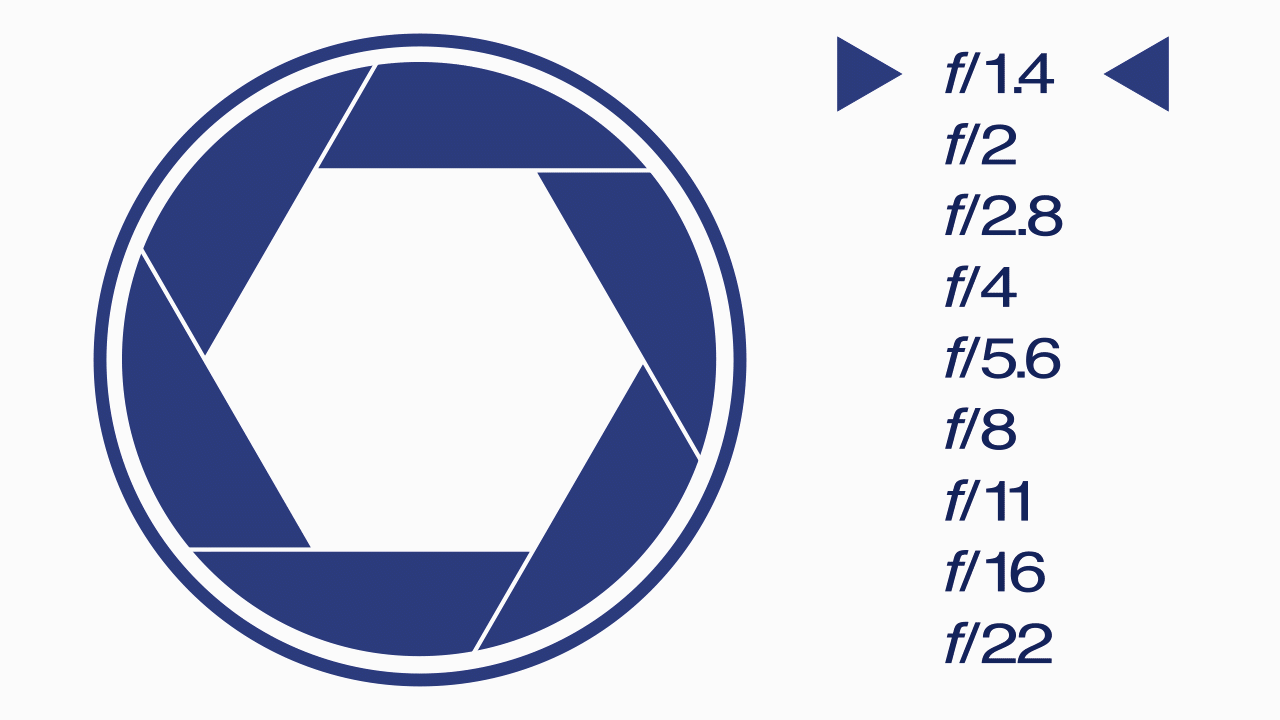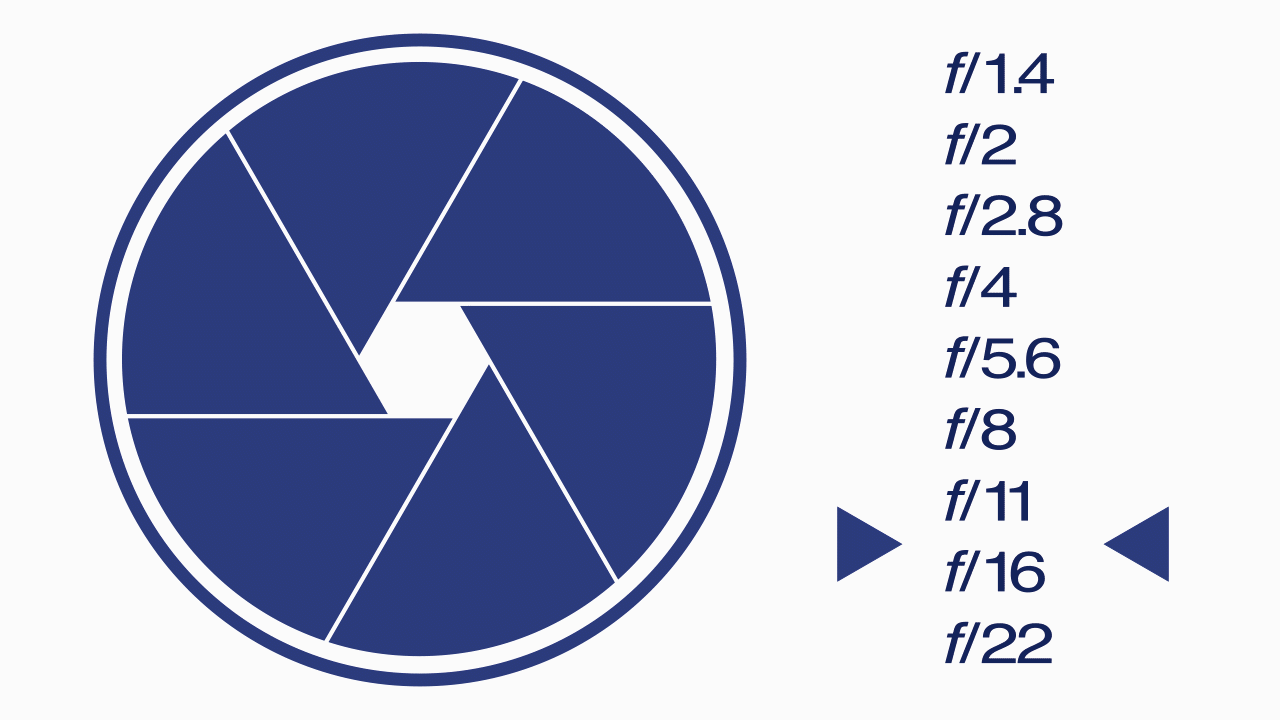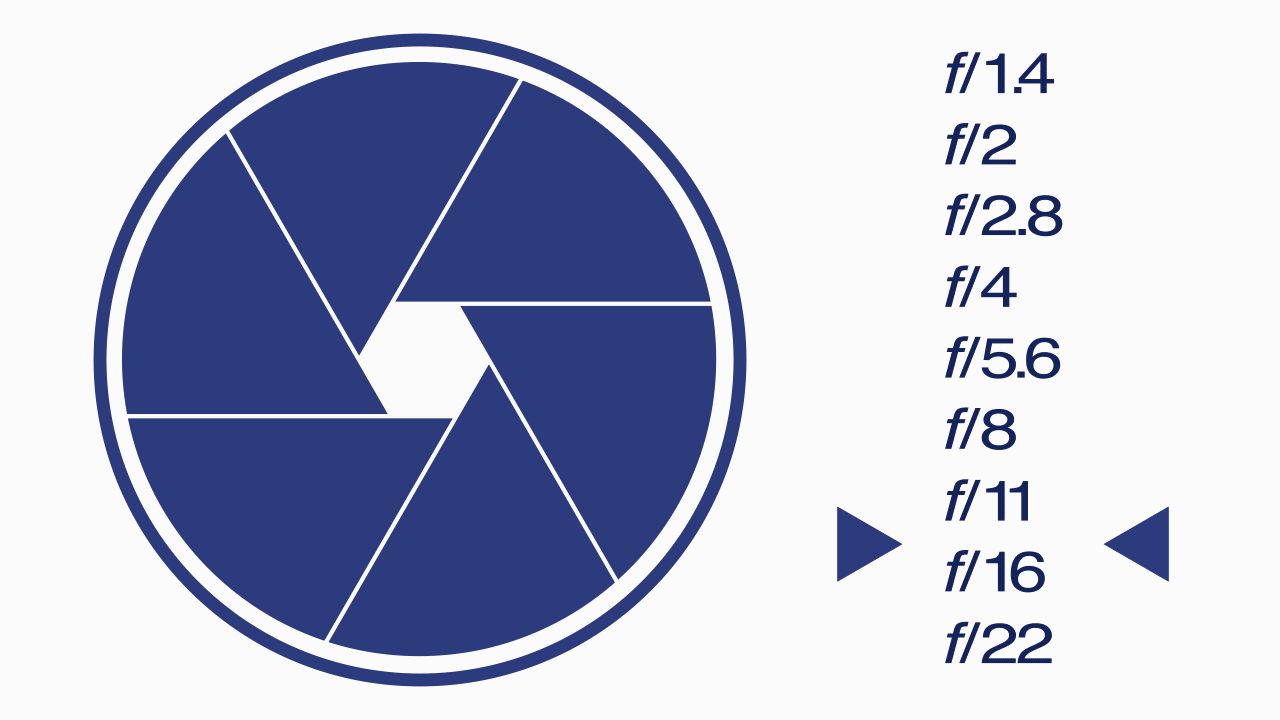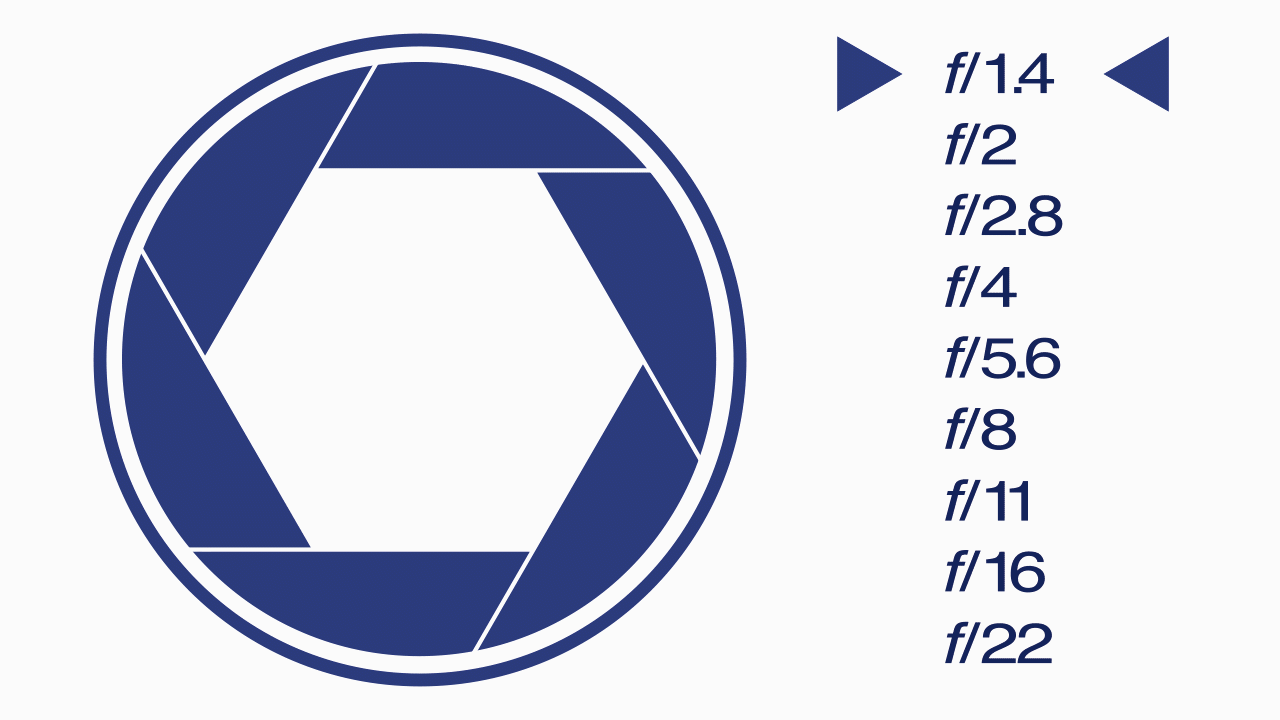
F-Stops
A camera setting that specifies the aperture of the lens for a particular shot and represented by using a table of f-numbers. The “f” refers to the focal length of the lens.

Gaffer
This person is the head electrician or lighting technician on a film set, responsible for the design and execution of a production’s lighting plan for the film.

Genre
Types or categories of film, used to classify films by theme and tone, such as musicals, thrillers, science fiction, Westerns, etc.

Graphic Match
Images placed back-to-back to frame an object in successive shots. This was used in Alfred Hitchcock’s “Psycho”, where the camera cuts from the character Marion Crane’s eye line to the shower drain, and the circumference and location of these two spheres in the frame are identical. Shots may dissolve into the next (plastic dissolve) or placed back-to-back (plastic cut).
Image Src: https://gifer.com/en/MPLQ

Greenlight
The go-ahead term for a film to begin production and be made.
Grip
This is the person responsible for the adjustment, set-up, and maintenance of all the production equipment on set.

Handheld Shot
A shot made by a camera that is held in hand or mounted on the cameraman’s shoulder, rather than using a stabilizing fixture.

Hays Code
Named for Will Hays, this was a series of rigorously enforced from the mid-1930s to the late 1960s.

Head-On Shot
The scene is filmed from above, often to make the subject or subjects look smaller on screen.

High-Angle Shot
A shot that films the scene from above, often to make the subjects or objects appear smaller.
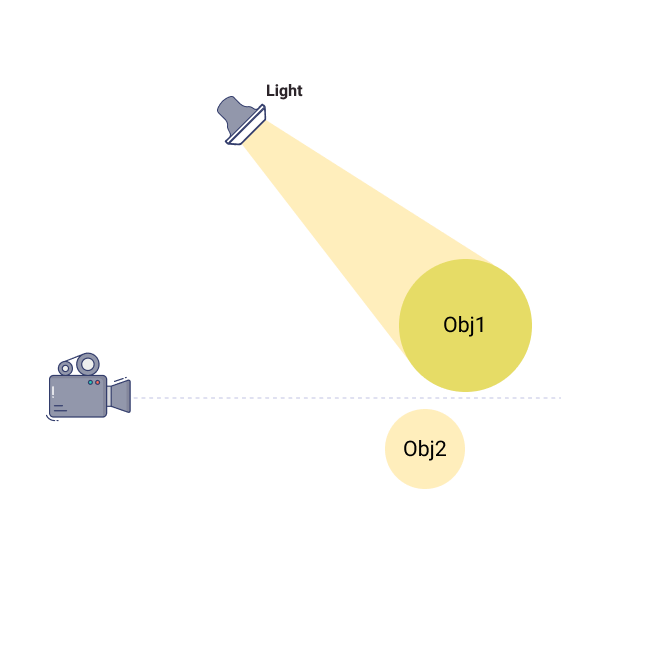
Highlighting
When you use beams of light for illuminating particular aspects of a subject or object.
Hitting a Mark
This is an actor’s term for moving in the correct positions on set, during rehearsals and camera takes. Using marks, or pieces of crossed tape on the ground, makes it easier for the camera to track and record the action.

IMAX
A large-screen film format that is around 10 times larger than the traditional cinema screen format, giving you a screen that is about eight-stories high. This type of screening produces incredibly high-definition sharpness for films.

Insert Shot
This is a shot that contains a particular visual detail that is inserted into a scene for informational purposes or to provide dramatic emphasis. The shot is almost always a close up shot.

Intellectual Montage (or Thematic Montage)
This type of editing uses justaposition or collision of contrasting shots or sequences to generate the idea of a greater relationship in the viewer’s mind. Intellectual montage was often used in the works of filmmaker Sergei Eisenstein. For example, if a shot of a man juxtaposes with a shot of a peacock, it could infer the idea of a vain person.

Intercut Shots
This usually refers to a series of shots, consisting of two simultaneous events, that are alternatively cut together to create suspense.
Into Frame
Referring to when an object or person moves into the picture without the camera moving, similar to a character coming on stage during a play.

Iris Out
This is when you end a scene with a closing circle or vignette that comes in from the edges of the screen, a transition similar to the look of an eye’s iris contracting.
Image Src: https://gifer.com/en/Diip

Jump Cut
An abrupt transition that breaks up a continuous shot. It has the effect of disorientating the scene and disrupting the narrative, and when the action returns it has noticeably advanced in time.
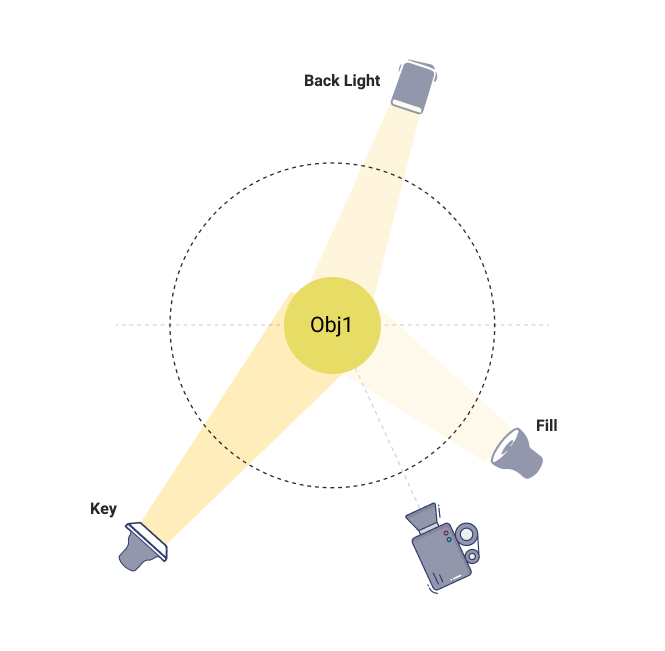
Key Light
This refers to the main or primary light on a subject, often angled and off-center that selectively illuminates various prominent features of the image to produce such specific things as depth and shadows.

Landmark Film
A ground-breaking or revolutionary film, either for its technical or performance artistry. These types of films are recognized by the National Film Registry.

Lap Dissolve
The method of transitioning between two scenes by fading out of the first scene into the next one.
Image Src: https://gfycat.com/likabledevotedbarebirdbat

Laserdisc (LD)
This is an optical disc format for analog video. This format was replaced after the introduction of a DVD in 1997, and by mid-2000 most studios and distributers stopped deploying their films in Laserdisc format.

Lens
The optical device used by the camera equipment to focus an image onto film stock.

Letterboxing
This is the process of shrinking the film image just enough so that its entire width appears on TV screen, with black areas above and below the image, emulating the widescreen format seen on TV screens.
Lighting
Lighting is often dependent of what type of film stock is being used, or the theme and tone of what the film’s narrative is trying to convey.

Line Producer
This person is responsible for managing all people and expenses while the film is being produced.

Lip Sync
This is the synchronization between the sound and its source in the film, and they are out of sync if they do not match.

Location
Any place a film is shot, other than in the studio or on the studio lot. When shooting is done in actual real world settings, shooting is called on location.

Locked-Down Shot
The method where a scene is filmed by a fixed camera to keep the image motionless

Logline
A short, introductory summary of a film’s story usually found on the first page of the screenplay. This is read by executives, judges, agents, producers and script-readers, and is important for writers to sell their scripts.

Long Shot
A shot that reveals the subject in their entirety, with them filling most of the frame.

Long Take
This is a shot of an unusually long duration, a significantly longer take than the average. Historically, the average shot length was 8.4 seconds, and Robert Altman’s “The Player” and the opening shot of Orson Welles’ “Touch of Evil” utilize long takes.

Low-Angle Shot
When a scene is filmed from below to make the subject or subjects appear larger on screen.
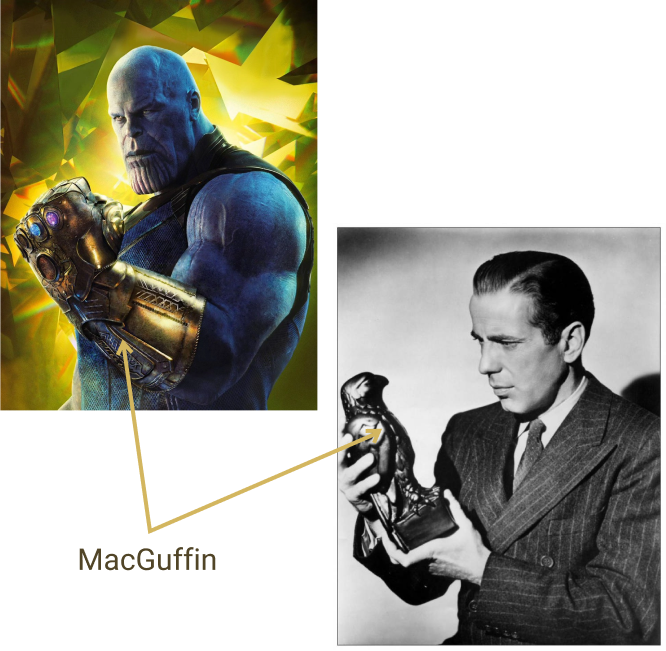

MacGuffin
A term coined by Alfred Hitchcock for a plot element or device that drives the action or logic of the plot. It is extremely important for the characters, but it is often ignored once it serves its purpose, such as the sled in “Citizen Kane”.

Master Shot
This refers to the long take of an entire scene, a long shot that that allows for later inspection of the components of the scene.
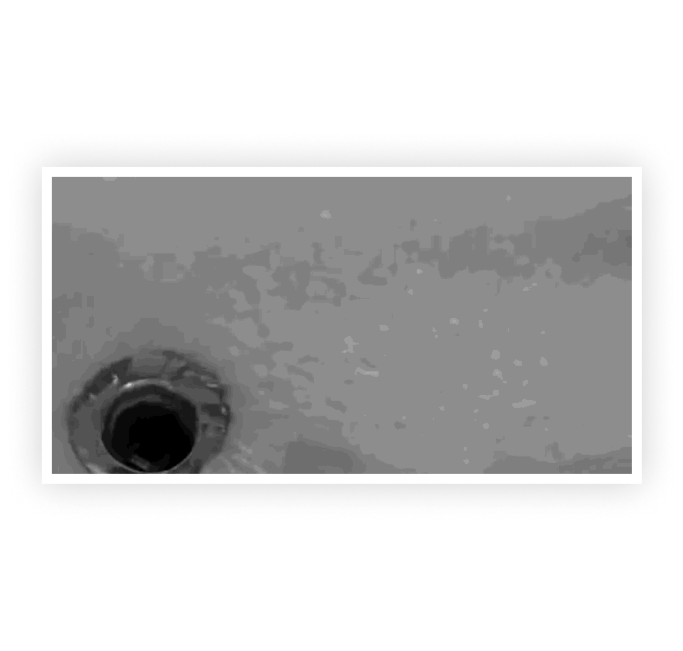
Match Cut To
A cut or transition between two unrelated objects to establish physical or metaphorical continuity or comparison.

Matte
A mask that obstructs some amount of light that passes through the camera lens. Mattes can take the form of a specific shape, such as a keyhole or star, which can then be imposed on the film as a blank area while the images are exposed. Instead of being mounted directly onto the camera, mattes are mostly produced with laboratory or technical methods.

Medium Shot
This camera shot is taken from medium distance and typically shot above the waist. This angle lets viewers see body language but not facial expressions.
Mise-En-Scene
Referring to the arrangement of all set elements in front of the camera to be filmed. This includes the settings, props, costumes, makeup, lighting, arrangement of actors, etc.
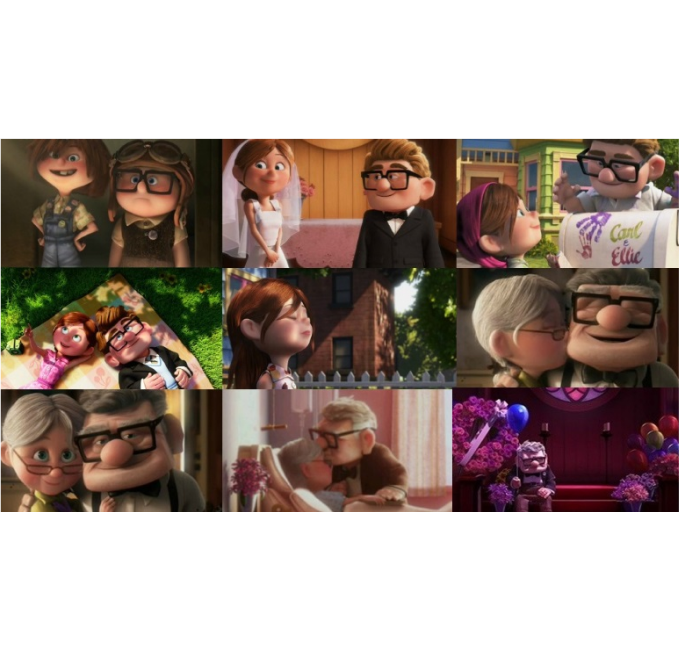

Montage
This refers to a film technique for putting together a series of short shots that create a composite picture. Montages are often used to show the passage of time in action.

MPAA
The acronym for the Motion Picture Association of America, an organization that looks out for the interests of lead film studios, and is also responsible for film ratings.

Multimedia
Describing the combination of audio, video, graphics, etc. An ambiguous term that includes presentation, editing, and interactivity.

Narration
Narration is important to film storylines, as it gives supplemental information to the audience by a voice offscreen. The narrator can either be a character in the movie or an omniscient presence.
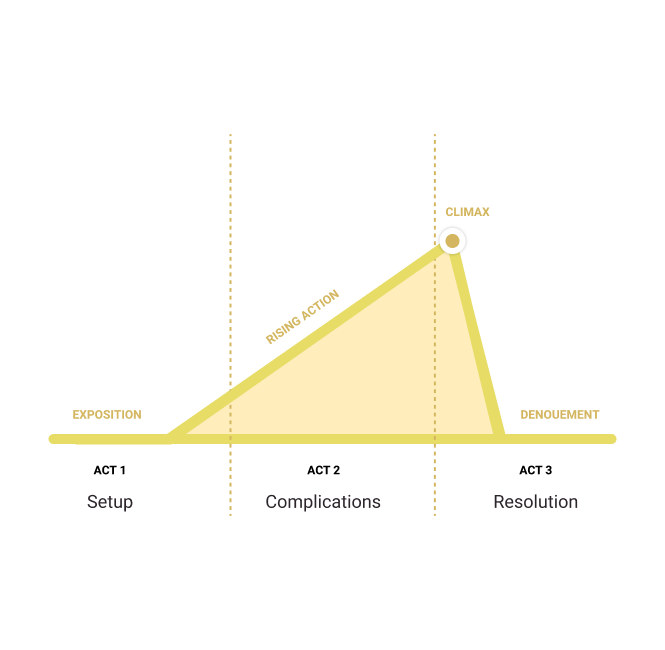
Narrative Structure
This refers to the organization of a film’s narrative building blocks based on the order of scenes in the screenplay. Screenwriters often utilize a three-act structure for narrative construction—the setup, the complications, and the resolution.
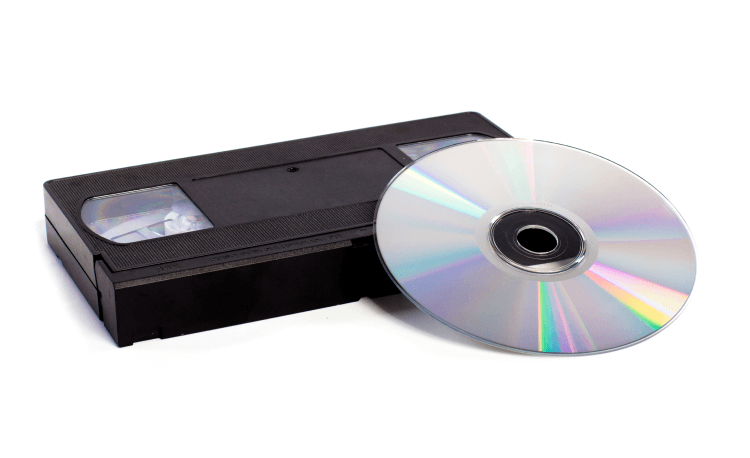

New Media
A form of media technology or communication that enhances, alters, or surpasses already-existing technology. For example, DVD and digital technology was built off analog technology such as VHS and Laserdisc.
Non-Diegetic Sound
Any sounds, such as underscored music on the soundtrack, that is not part of the world of the film’s narrative. In other words, the characters in the story do not hear it, and only the audience can.

Non-Linear Editing
This is random-access editing of film or audio on a computer rather than physically editing the film by cutting the stock. Non-linear editing systems include Media 100 and AVID, whereas non-linear software packages include Final Cut Pro and Adobe Premiere.
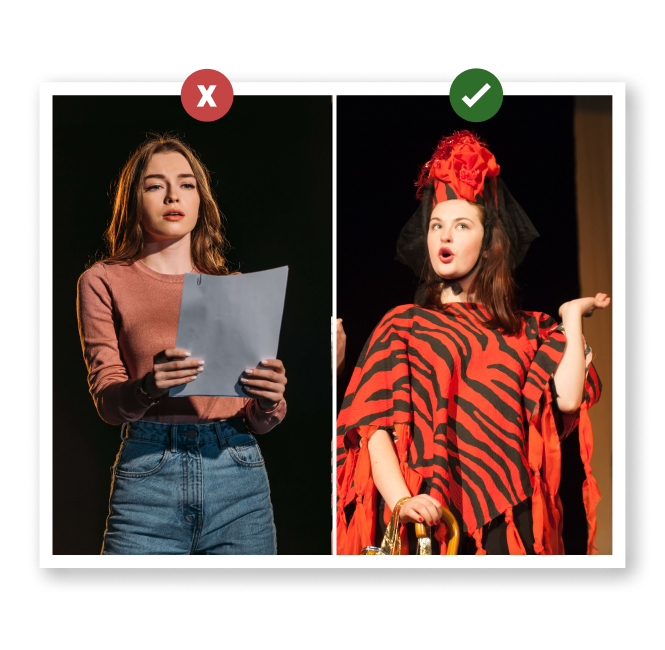

Off Book
Referring to when an actor has completely learned their lines, and no longer needs to hold a script on set.

Off-Screen Dialogue (or Off-Camera Dialogue)
This is dialogue spoken by a diegetic character not seen on set in a specific shot, but different than a voice over.
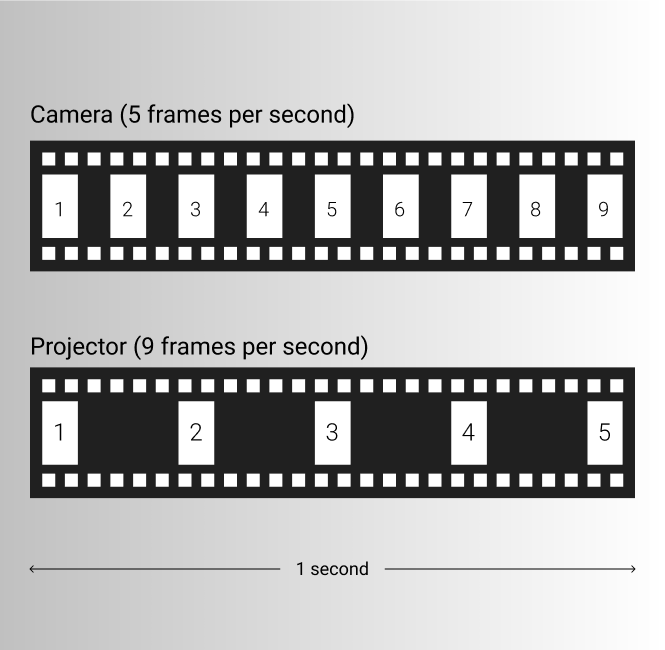
Overcranking
The process of speeding up the frame rate in a camera, so that when the images are played at normal frame rate the action appears in slow motion. The term has its roots in early film making where the cameras used a crank handle to roll the film.

Overexposed
This refers to a type of shot that has more light than other types, resulting in a washed-out, blinding effect. It is typically used for dream or flashback sequences.

Over the Shoulder Shot
Useful in dialogue scenes, this is a medium shot that allows one actor to be filmed head-on from over the shoulder of another actor.
Pan
Camera movement around the imaginary vertical axis that runs through the set and camera location, either from right to left or from left to right.

Pipeline
The schedule of movie projects in production.
Point of View Shot
This type of shot is taken from the vantage point of a character in the film, and can also be known as the first person camera.

Positive Print
The original light image captured on film.

Post-Credits Sequence
An epilogue or throwaway scene that comes after the end credits of a film. These are famously used in Marvel movies, where an extra scene after the credits creates hype for the next installment in the franchise.

Post-Production
This refers to the to the work performed on a film after the conclusion of principal photography, usually involving picture and sound editing and effects.

Prime Lens
A single focal-length.

Pull Back
The shot where the camera physically moves away or zooms out from the subject or object to reveal the entire context of the scene.
Push In
The opposite to a pull back, this is a shot where the camera moves in closer or zooms into a subject or object.

Rack Focus (or Search Focus)
The switching of focus during a shot from one subject or object to another, for instance filming a conversation between two actors that are in the same frame, but in different areas of foreground and background.
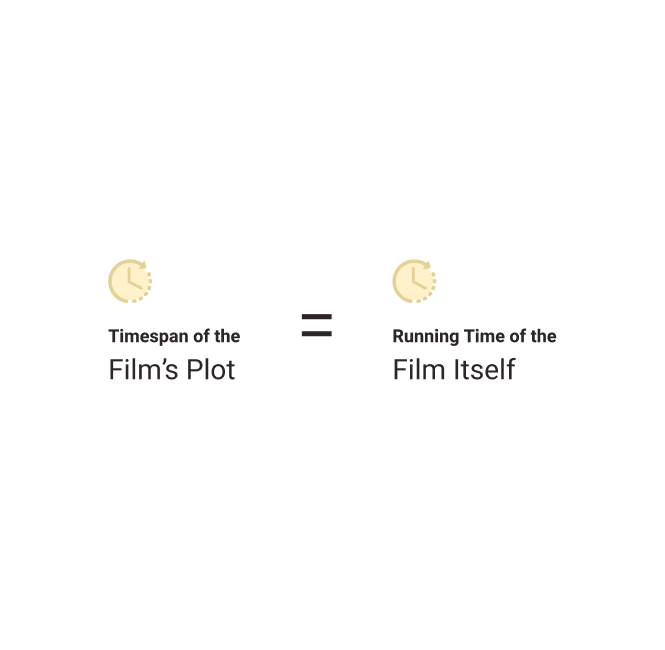
Real Time
When the timespan of the film’s plot is the same of the running time of the film itself, it is known as real time. This is contrasting to filmic time where intervals can be sped up or slowed depending on what the plot needs.
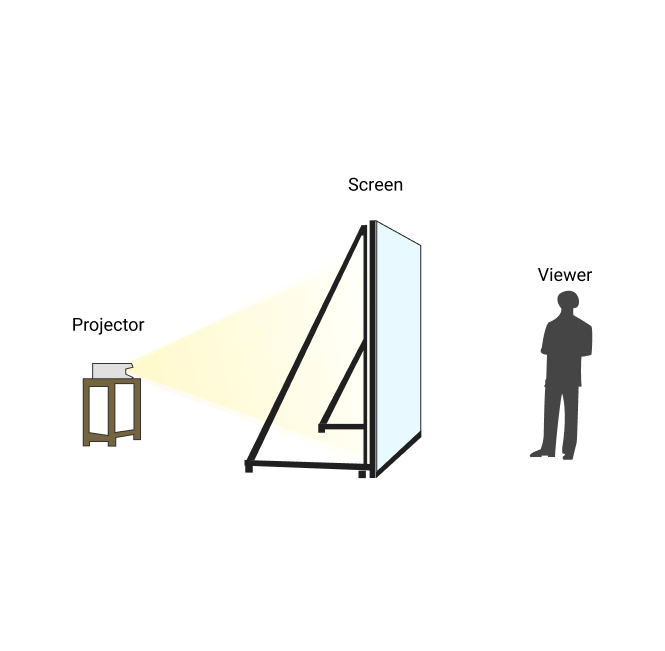
Rear Projection
The technique where all elements of the set are in front of a translucent, blue, or green screen on which a picture is projected from behind, like in Alfred Hitchcock’s film “Vertigo”.

Reel
This term has two meanings:
1. The physical object on which film is wound.
2. The units of film length or time on a given reel.

Reflexivity
This term refers to self-consciousness in a film that draws specific attention to its own construction. Such films try to remind the audience that they are indeed watching a film, so that they can focus on formal, social, or political implications of the film.

Reverse Angle (or Reverse Shot)
This refers to a shot from the opposite side of a subject. And in a dialogue scene, it is usually a shot of the second participant in the conversation.
Reverse Motion
Referring to screen action that runs backwards.

Riggers
These workers are responsible for the setting up of lighting equipment and scaffolding structures on film sets.

Scene
The process of slowing the camera’s frame rate, so that when the images are projected on screen at a normal frame rate the action appears to be in fast motion.

Screenplay
The script written to be made into a film
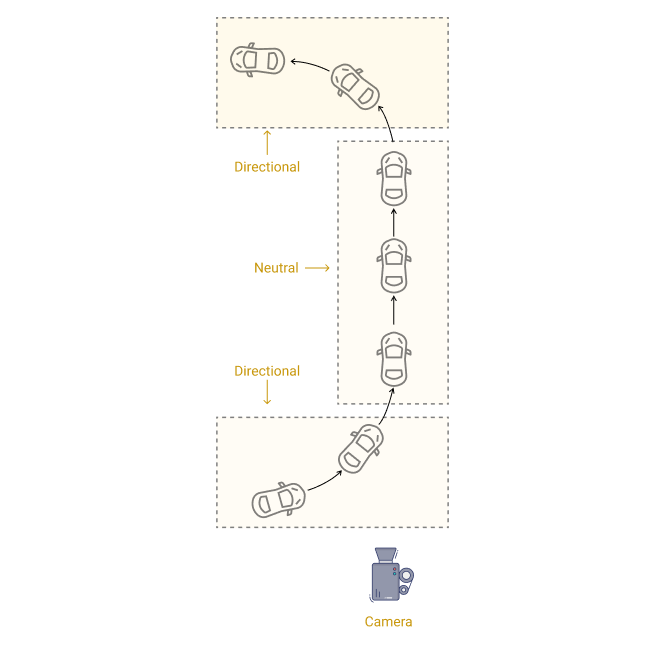
Screen Direction
Whatever direction the subject or object is looking at or moving towards, as described from the audience’s point of view.

Screen Time
Duration of an action as allocated by editing, as opposed to real time.

Screenwriter
The writer who either writes screenplays or adapts stories for film.

Sequence
A dramatic unit comprised of shots or scenes linked together by a common idea or image, sequences can span varying times and locations as long as the dramatic structure and elements remain intact.
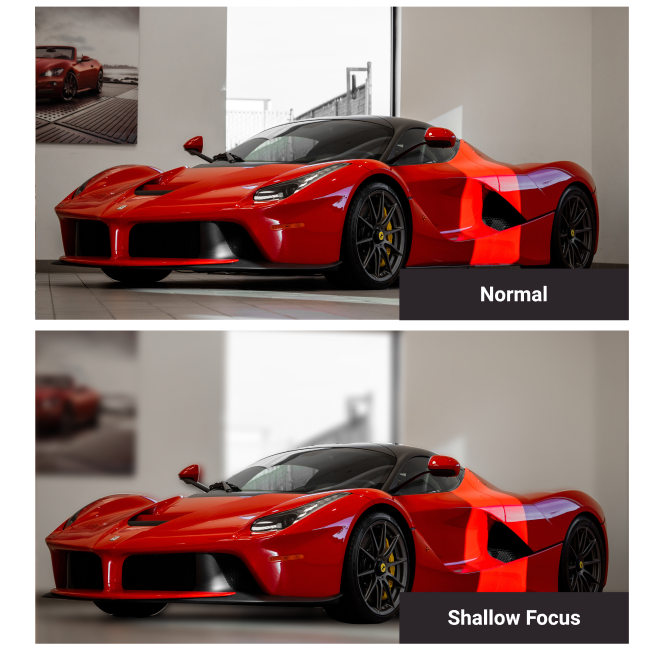

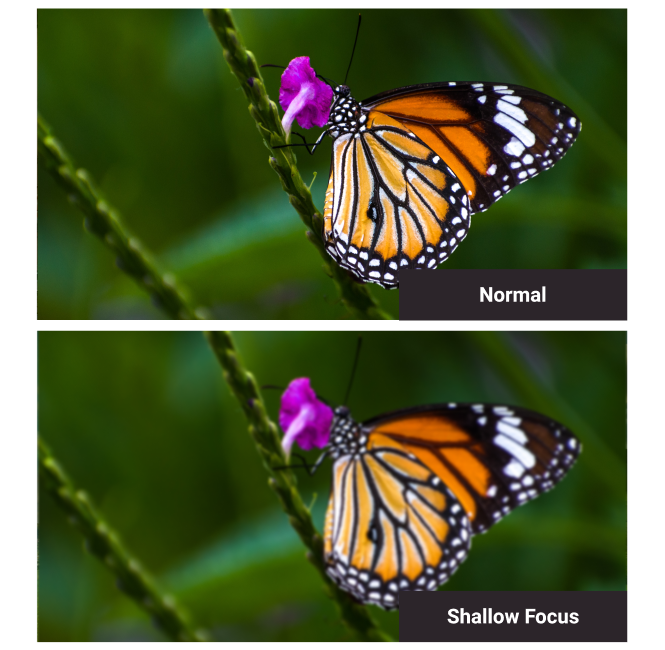
Shallow Focus
When subjects or objects on only one plane are in focus, with the others in the background or foreground are out of focus to the camera.

Shooting Script
This is the term used for the final script used for the filming process.
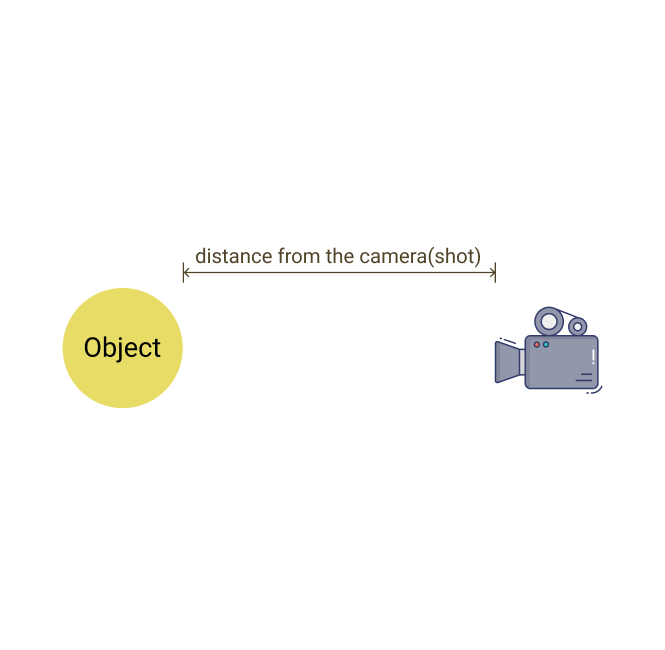
Shot
This refers generally to the camera distance with respect to the subject within the shot. There are 7 basic types of shots that are quite self-explanatory, including extreme close-up, close-up, medium close-up, medium shot, medium long shot, long shot, and extreme long shot or distance shot.
Shot List
The list provided to the film crew that describes all the shots that the director wants to get done that day, often given out the day before shooting.
Image Src: https://www.techsmith.com/blog/shot-list/
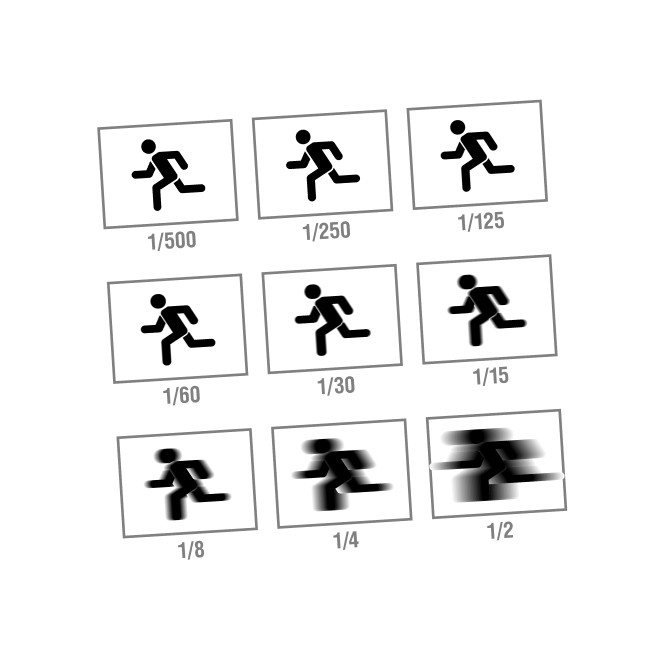
Shutter Speed
Referring to the length of time in which a single frame of film is exposed. A traditional shutter angle is 180 degrees, while the film itself is exposed for 1/48 second at 24 frames.
Smash Cut To
Referring to the length of time in which a single frame of film is exposed. A traditional shutter angle is 180 degrees, while the film itself is exposed for 1/48 second at 24 frames.

Soft Focus
The visual effect that uses filters or shooting with an out-of-focus lens, in order to produce a blurry shot.

Soundstage
This is a large area (usually within a studio) where elaborate sets can be built and maintained during film production.

Spec Script
A non-commissioned script sent to studios for their consideration.

Static Shot
The shot created by using an immobile camera.

Stock Shot
This refers to previously recorded footage that can be edited into the film. Footage can include historical events or animal shots.

Stop Motion
This is a form of animation where objects are filmed frame-by-frame and moved slightly between shooting each frame, in order to create the illusion of the object’s movement.
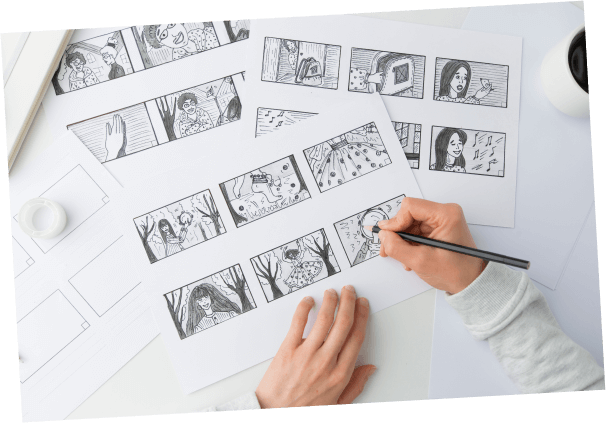

Story Board
A sequential series of sketches or stills that show what will happen in the film, providing both a rough synopsis and an outline of what shots and angles the camera lens will be filming.
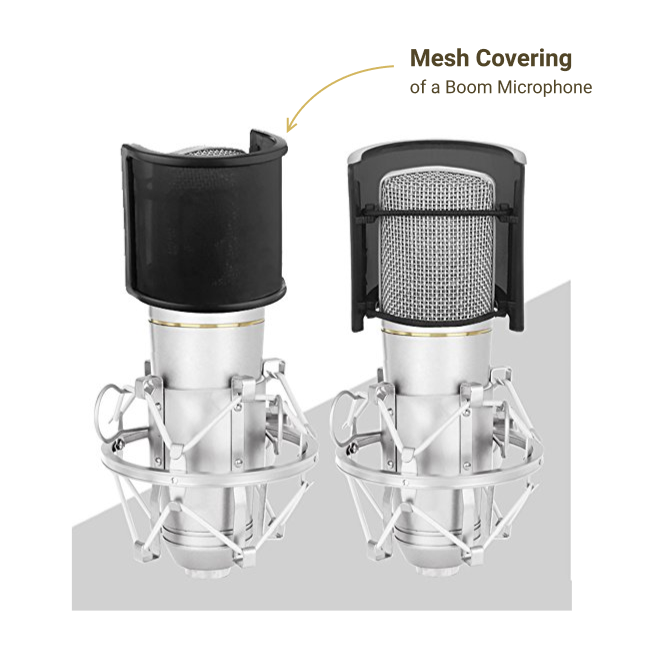

Strike the Puffin
The process of replacing the mesh covering of a boom microphone.
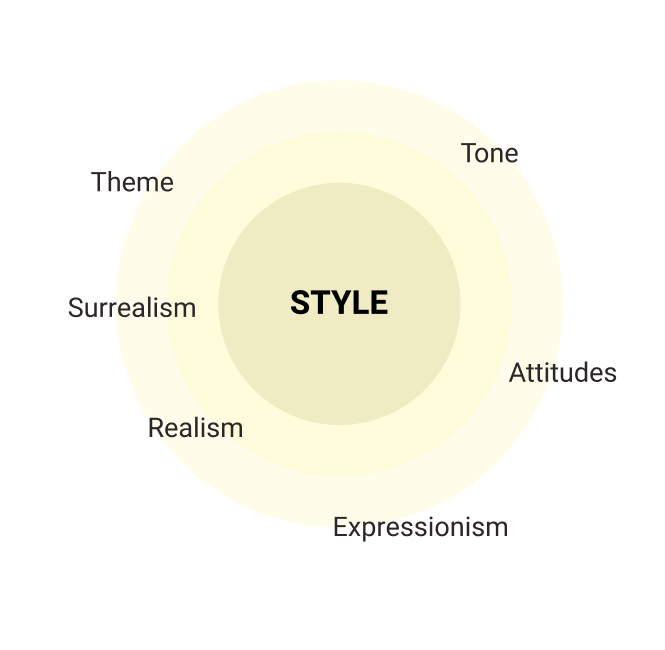
Style
The manner in which a film conveys theme, tone, ideas, and attitudes towards the material in cinematic terms. There are broad style types like realism, expressionism, surrealism, etc., but each filmmaker will interpret the script they are working with in their individual style and make their own directorial choices. A film’s style is also influenced by budget, country, artistic choices, time period, conventions, and mode of production.
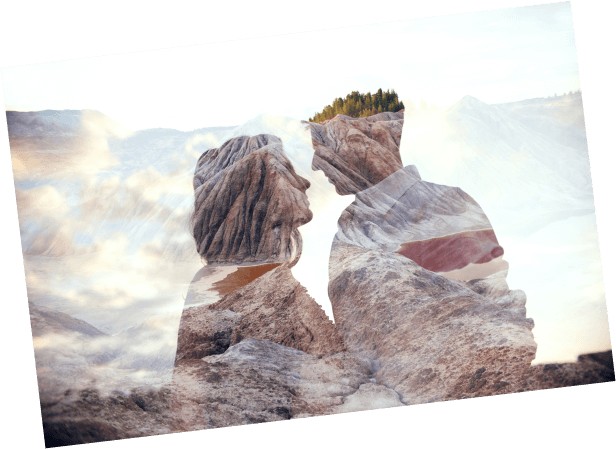

Superimposition
Multiple exposure where two or more images are visible over each other simultaneously.
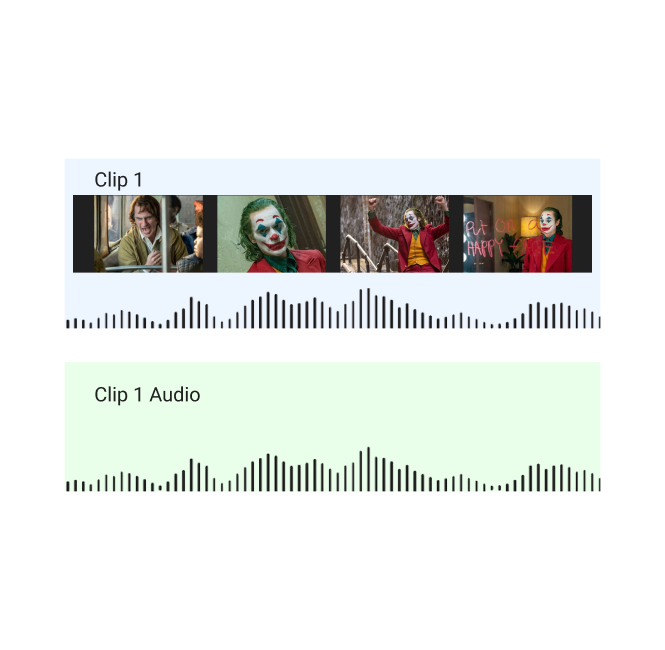

Sync (or Synchronism)
This refers to sound that is matched with the movements that occur in the images filmed, like when dialogue corresponds to lip movements on the screen.

Tagline
A short sentence or phrase that summarizes the film to a general audience, teasing what the film is about and is usually quite clever and memorable. For example, in “Alien”, the tagline for the film is “In space, no one can hear you scream.”

Take
A take is one run of the camera as it records a single shot. Typically, each of these shots are filmed multiple times, and the best version or take of each shot is chosen for the final film.
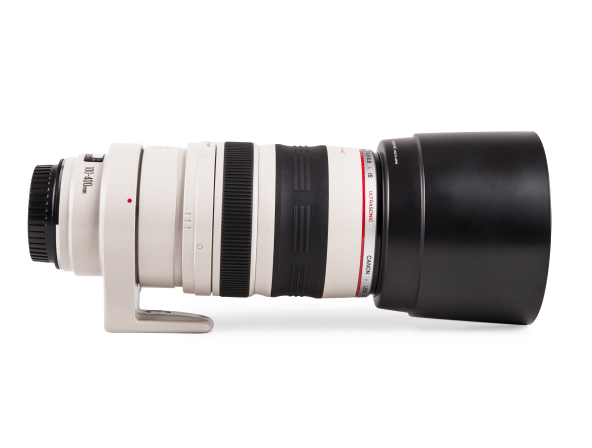

Telephoto Lens
A specific camera lens of a long focal-length with a narrow angle of view. This lens condenses space being filmed, flattens depths, and brings distant subjects and objects close.

Theme
The overarching idea a film tries to convey, as opposed to the plot of a film which conveys the action of what happens.

Theory
This is the philosophical or aesthetic model applied to cinema that tries to explain the characteristics and nature of film in general or of a particular film.
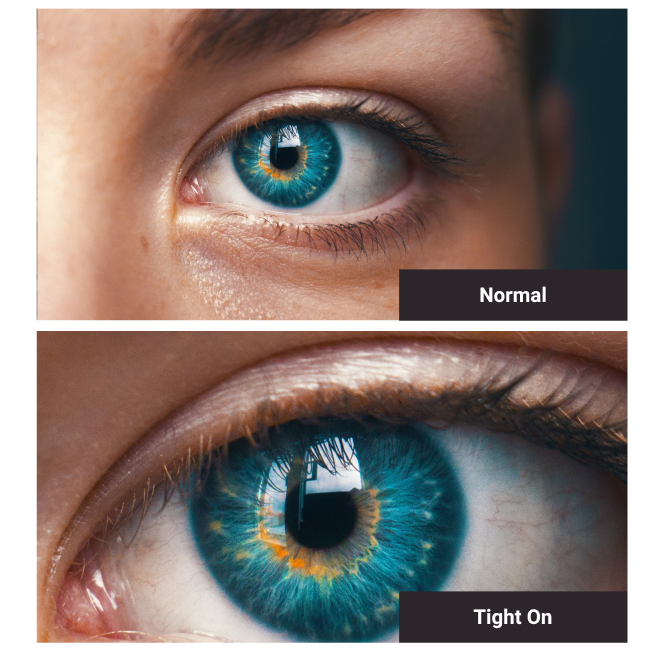
Tight On
The close-up shot of a subject or object
Tracking Shot
This type of shot follows a subject or object, and often involves mounting a camera onto a dolly and moving it along a dolly track.

Treatment
This term refers to an abridged script that is longer than a synopsis, consisting of summaries of each major scene in the film, and might include pieces of dialogue.
Undercranking
The process of slowing the camera’s frame rate, so that when the images are projected on screen at a normal frame rate the action appears to be in fast motion.

Underexposure
The process of slowing the camera’s frame rate, so that when the images are projected on screen at a normal frame rate the action appears to be in fast motion.

Unreliable Narrator
The unreliable narrator is a character whose perspective the viewers follow for the narrative, but who also lacks credibility. Unreliable narrators could either lack the entirety of the information needed to tell the story, or they have a complete bias.

Vertigo Effect (or Contrazoom)
This camera technique was created by Alfred Hitchcock during the filming of his classic “Vertigo”. This shot involves the camera tracking backwards while zooming in at the same time, making the subject or object seem stationary while their surroundings on set change swiftly.

Video
This refers to the picture portion of a TV picture signal or the electronic signal that makes up a TV picture. Video formats include Beta, Digital Video, HIS, Mini-DV, and VUS.
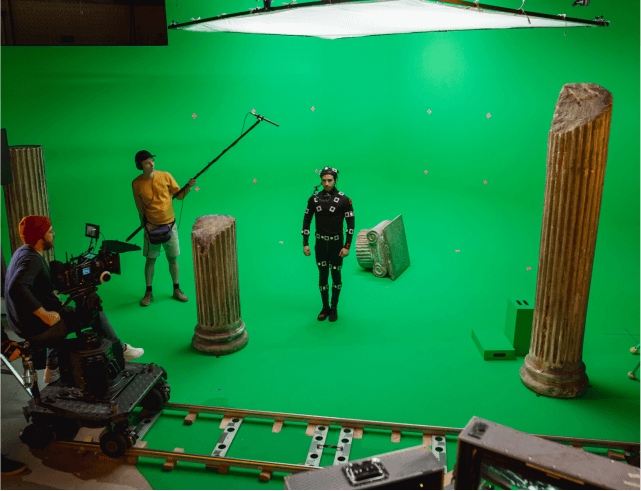
Visual Effects
Anything added to the film that was not contained in the original shot falls under the classification of special effects. Either through CGI or special techniques, visual effects are a common phenomenon in modern filmmaking.
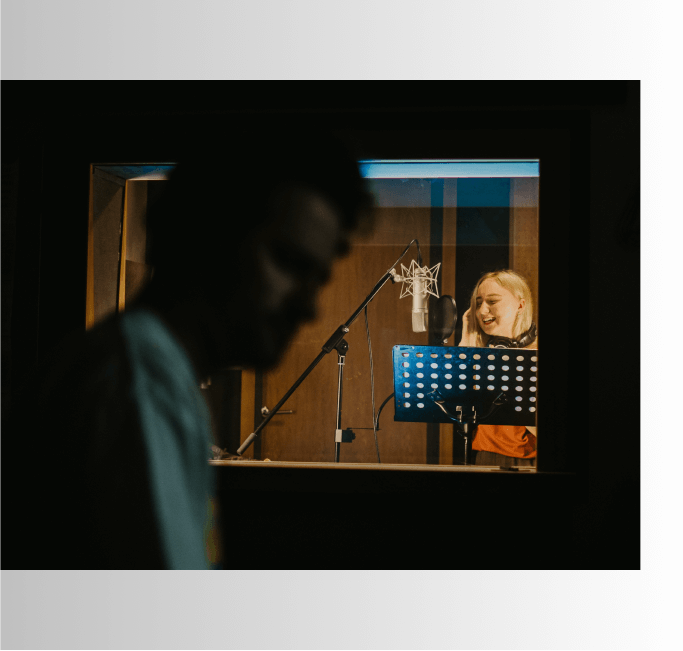

Voice-Over
This refers to having dialogue, usually narration, that comes from offscreen and is an unseen voice, narrator, or character.
Walk-On
A minor role in film that is a single, brief appearance onscreen without dialogue, and not appearing in the credits. Different than extras, who are typically onscreen for longer.

Wardrobe
A generalized term for the costume department for films and film sets. Wardrobe can also be used to refer to an individual actor’s costume and all the accoutrement that goes with it.
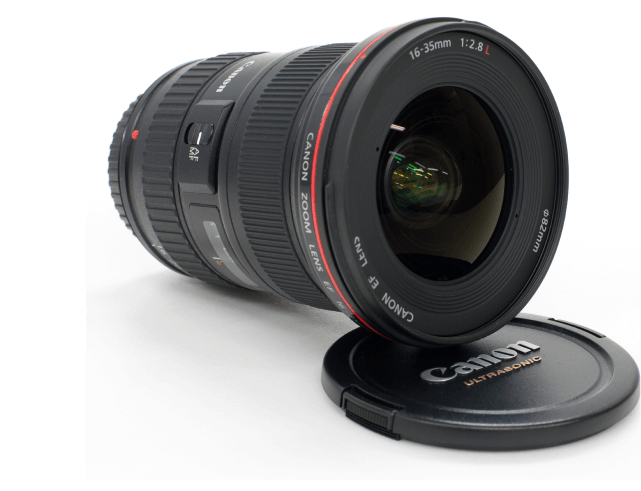

Wide Angle Lens
A specific camera lens of short focal-length with a broad angle of view, exaggerating depth of space.
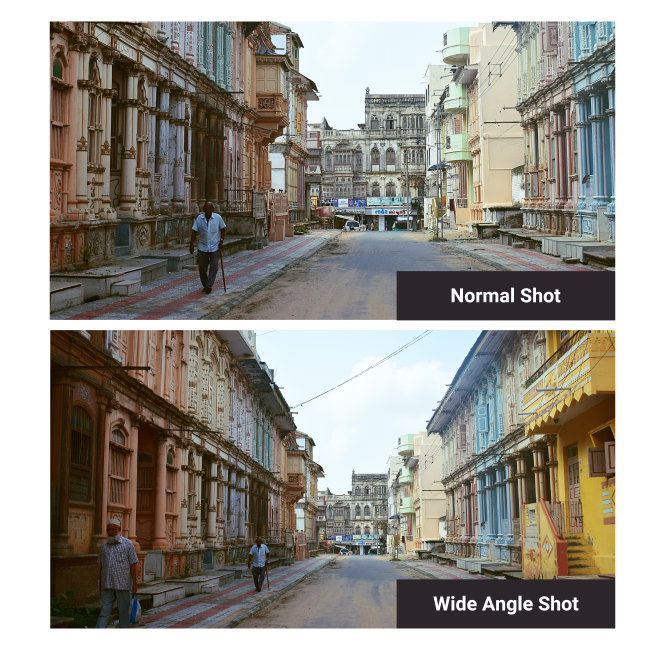

Wide Angle Shot
This is a shot from a particular camera lens that is able to capture a wider field of view than a regular lens. Such shots work to exaggerate the disparity, depth, and distance between background and foreground, while keeping all objects in focus and in perspective.

Wrap
The term that refers to the completion of shooting, either for the single day or for the entire production. This term has its roots in the earlier days of filmmaking, where cameramen would say “wind, reel, and print”, which later became abbreviated as “wrap”, and is still used today.

Zoom
This is the movement of a lens of variable focal length, able to be altered during shooting. This enables a smooth transition from wide-angle to telephoto shots without actually having to move the camera.

Zoom Shot
The shot that plays with the magnification of subjects or objects by increasing (zooming in) the focus of camera lenses or decreasing it (zooming out).
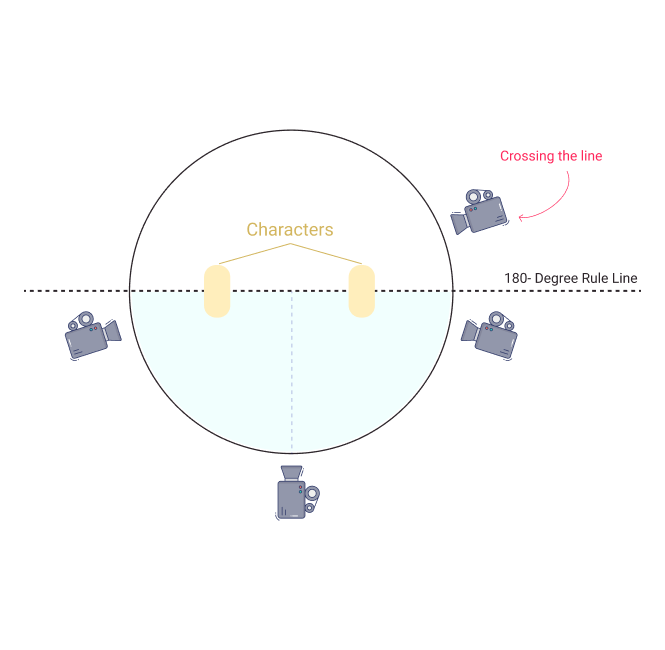
180- Degree Rule
This rule essentially keeps the camera on one side of the action, keeping characters grounded compositionally on one side of the frame.

3-D Film
3-D film uses a three-dimensional, stereoscopic form that creates the illusion of depth and a more immersive film experience.

